Make some changes to the world environment
-
Building 3, Wanyang Innovation City, Langxia Street, Yuyao City, Zhejiang Province

Fitting 6 AWG Wires in 1″ Plastic Flex Conduit
Have you ever wondered how many 6 AWG wires fit in a 1″ plastic flex conduit? Knowing about electrical conduit installation and wiring installation guide matters a lot. It’s not just about following the National Electric Code (NEC). It’s also about making sure your electrical system works well and lasts a long time.
Based on the 2017 NEC, how much you can fit in conduits depends on the material. In a 1″ EMT conduit, you can safely put 26 6 AWG wires, but a 1″ galvanized pipe conduit1 only fits 10. It’s vital for professionals like us to understand these rules. This way, we can make our installations as good as they can be.
This guide is for both experienced electricians and beginners. It gives detailed info on how to put 6 AWG wires into a 1″ plastic flex conduit. We’ll go over the steps one by one. This will make sure you meet the latest NEC standards. Your electrical projects will be safe and work great.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the importance of conduit fill calculation for safety and efficiency.
- Discover how many 6 AWG wires can fit into a 1″ plastic flex conduit.
- Learn to navigate NEC standards for compliant wiring installation.
- Gain insight into comparing different types of conduits like EMT, IMC, and galvanized pipe.
- Get step-by-step guidance on ensuring optimal wire and conduit compatibility.
For more details and practical tips, check out our full guide on single screw plastic extruders. This info adds to what we know about conduit fill and how to fit wires right.
Understanding Conduit Fill Calculation
Conduit fill calculation is crucial for safe and efficient electrical setups. It helps us meet the National Electrical Code (NEC) and maintain high safety standards.
Why Conduit Fill Matters
Calculating conduit fill right stops overheating and reduces fire risks. Too many wires in a conduit can overheat, causing system failures and damaging wire insulation. This shortens the electrical system’s life2. Following the rules keeps systems safe, reliable, and easy to manage3.
Basic Principles of Conduit Fill
The NEC sets limits on how much a conduit can be filled. No more than 53% for one wire, 31% for two, and 40% for more than two4. To figure out how much space wires take, we use a formula based on wire size4. This ensures our work is both efficient and follows rules.
Safety and Compliance with NEC
Following NEC rules is essential for safety. The NEC gives us guidance to manage heat and prevent wire damage. This helps avoid short circuits and other dangers2. Knowing how many wires fit in a conduit keeps systems safe and working well2.
The NEC also has detailed charts in Chapter Nine for different conduits. This makes sure each setup meets safety standards4. Sticking to these rules is key for safe, lasting electrical systems.
Wire Gauge and Its Significance
Wire gauge is very important in electrical systems for keeping things safe and working well. The National Electrical Code shows that using the wrong wire gauge can cause big problems. This includes wires getting too hot and serious dangers. So, picking the right wire size is key to any electrical setup.
Defining Wire Gauge
Wire gauge means how thick an electrical wire is, which affects how much electricity it can carry. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) system is used to measure this. In this system, a smaller number means a thicker wire that can carry more electricity. For instance, a 6-gauge wire is thicker and can handle more power than a 12-gauge wire.
Importance of Correct Wire Gauge
Choosing the right wire gauge is critical. The right gauge keeps things safe and meets the National Electrical Code (NEC) standards. The gauge you need depends on how much current is needed, how many wires you have, and where you’re installing them. The NEC has a rule that says only 40% of a conduit can be filled with three or more wires5. This is to avoid wires getting too hot and to make the system last longer.
Common Wire Gauges in Electrical Installations
There are some wire gauges that are often used in homes, shops, and big buildings. Let’s look at some common types and what they’re for:
- 14 AWG: Used for lighting in homes.
- 12 AWG: Good for power outlets and lights.
- 10 AWG: Works for air conditioners and water heaters.
- 8 AWG: Used in big appliances like stoves.
- 6 AWG: For big jobs like sub-panels and main entrances.
Picking the right wire gauge is vital when setting up electrical systems. You must consider what the wire is used for and follow the codes. This makes sure the setup is safe, works well, and follows the rules about wire sizes.
Types of Conduit Used in Wiring
Choosing the right conduit for electrical wiring projects requires understanding the differences between metal and plastic types. Each has its own benefits and best uses based on the project’s needs, where it will be installed, how long it needs to last, and how much it costs.
Metal vs. Plastic Conduit
Metal conduits, like EMT, IMC, and GRC, are often used in commercial projects because they’re strong and meet high safety standards. The market for Metal Electrical Conduit is expected to grow beyond USD 5.5 billion by 2032. This growth is thanks to new features, like being lighter and resisting rust6. Their popularity is also due to strict safety rules in businesses and more use of these conduits in trains and subways6.
Plastic conduits, on the other hand, are chosen for being flexible and less expensive. PVC, a type of plastic conduit, is especially good for burying directly under the ground in homes7. They are best for places needing protection against water and where easy setup is key.
Flexible vs. Rigid Conduit
Flexible conduits, both metal and plastic, are simpler to install in tricky layouts and when updating old systems. But, pulling cables through metal flexible conduit can damage them7. On the other side, rigid conduits offer better protection in tough settings and are trusted for strong, lasting installations. EMT, a kind of rigid metal conduit, is a favorite in commercial areas for its toughness7.
Choosing between flexible and rigid conduits depends on the specific needs of a project and the setting. Flexible conduits fit well in places that change often, while rigid ones are best for areas needing strong, long-lasting solutions.
Features of 1″ Plastic Flex Conduit
Knowing how 1-inch plastic flex conduit works is key to choosing the best type for your electrical needs. This type of conduit is often the top pick because of its flexibility and the benefits it brings. These make it super useful in many different wiring projects.
Material and Construction
The 1-inch plastic flex conduit is usually made from strong polypropylene or PVC. These materials are flexible and tough. Because of its spiral design, it’s easy to put through walls and tight spots. Perfect for tricky wiring jobs. Plus, it can handle chemicals and dampness, ensuring it lasts a long time in all sorts of places. Don’t forget to check out more on conduit material selection8.

Advantages of Plastic Flex Conduit
Plastic conduits offer big pluses. For starters, they are light, making them easier and cheaper to install than metal ones. They can also bend easily for any direction needed without breaking. Another plus is they don’t rust, keeping maintenance low. They’re also strong against UV rays, making them great for both inside and outside use. These benefits show why plastic conduit is so useful9.
Limitations and Considerations
However, 1-inch plastic flex conduit isn’t perfect. It’s not as protective as metal in places where damage is likely. And, it might not hold up in very hot conditions. Also, following the National Electric Code (NEC) is a must. It says when using three or more wires, the conduit should only be 40% full. This rule is crucial for safe and effective electrical setups10. So, think carefully when picking conduit for important electric jobs.
How Many 6 AWG Fit in 1 Plastic Flex Conduit
When figuring out how much cable can fit into a conduit, you have to look at a few things. These include the type of conduit and the size of the wire. Fitting 6 AWG wires into a 1″ plastic flex conduit needs careful planning. This makes sure everything is safe and follows the National Electrical Code (NEC).
The space a 6 AWG wire takes up is about 8.3 square millimeters11. Knowing this, you can work out how much space all your wires will need in the conduit. The NEC says the wires can only fill 40% of the conduit’s space11. This rule helps prevent wires from getting too hot by making sure there’s enough room for air to flow around them.
To safely fit several 6 AWG wires, you’d need at least a 1 1/4 inch diameter conduit11. But to make future work easier, or if you might add more wires later, people often use bigger sizes. Choices like 1 1/2 inch, 2 inches, and even 2 1/2 inches are common11.
Different types of conduits can hold varying numbers of 6 AWG wires. For instance, a 1 inch EMT conduit fits up to 35 wires. A 1 inch IMC conduit can carry 39 wires. Meanwhile, a 1 inch galvanized conduit can handle 36 wires1. This shows why picking the right size conduit is crucial. It’s not just about what you need now, but also planning for the future.
Checking conduit fill charts is a smart move before starting your project. Plus, detailed rules and data from the NEC Conduit Size Guide are very useful11. Following these guidelines ensures your wiring is done right, keeping it safe and up to code.
Steps to Calculate Conduit Fill for 6 AWG Wires
In this section, we talk about how to figure out conduit fill for 6 AWG wires. It’s about gathering all the info you need, looking at conduit fill charts, and making sure everything follows the NEC codes. This makes sure the electrical work is safe and up to standards.
Gather Necessary Data
To start, you need to collect some important information. This means knowing the wire gauge, how big the conduit is, and how many wires there are. Having the right data makes sure your calculations are accurate and the conduit isn’t too full. For example, a chart will tell you a 1″ plastic flex conduit can hold up to 3 wires of 6 AWG in a certain type of PVC conduit12.
Use Conduit Fill Charts
Then, you use conduit fill charts to figure out how full the conduit can be. The rules change depending on the conduit size and how thick the wires are13. For example, you can fill the conduit 53% full if you have one wire, 31% if there are two, and 40% if there are more. But, remember not to go over 60% full when adding more wires later13. Charts help ensure the conduit isn’t too crowded right away or in the future.
Verify Against NEC Code
Lastly, make sure your math lines up with the most current NEC code for safety and to follow the rules14. Following the NEC puts a standard in place for electrical work. The code says not to fill the conduit more than 40% at first and to keep safety margins in mind. This keeps electrical systems safe and working well. Make sure all files are set up right for a solid quote14.
By doing these steps—getting the right info, using fill charts, and checking the NEC code—your electrical projects will be both efficient and safe. Planning well and sticking to standards helps handle the tricky parts of wiring systems.
Understanding Conduit Fill Tables
Knowing how to use a conduit fill table guide right is key. It helps make sure electrical setups work well and are safe. We will look into using these tables and charts to not exceed the allowed space in a conduit.
Reading a Conduit Fill Table
To read a conduit fill table, you need to get several things:
- The size of conduits, ranging from 1/2 inch to 6 inches, depends on the electrical needs and how many wires15.
- Sizes like Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) help make sure everything fits right and stays safe15.
- Inches are used for measurements in the U.S., while Europe uses the metric system15.
- The thickness of the conduit walls, with types like Schedule 40 and 80 PVC, affects durability and wire protection15.
- Follow NE code for how many wires can fit in a conduit15.
- Consider the surroundings to pick the best conduit for protecting wires15.
These factors help ensure the conduit can carry enough wires safely and follows the rules. For instance, conduits under 3/4″ aren’t suitable for communication cables16. It’s crucial to choose the right conduit size for the system to work its best15.
Using Conduit Fill Charts Effectively
Here’s how to use a conduit fill table guide properly:
- Pick the conduit size and types of wires, for example, 1″ plastic flex conduit with 6 AWG wires.
- Find the right column in the table for your conduit size and wire type.
- Make sure not to fill more than 40% at first, and keep under 60% after that to avoid too many wires16.
- Adjust the wire jacket outer diameters to match the table exactly16.
- Use other charts, like a PoE chart, with your table for all cable calculations16.
For example, don’t put Ethernet and electrical cables together due to fire risks and signal issues16. Also, be mindful of size conversions for international projects, like turning 1 inch into about 25.4 millimeters15.
By doing these steps and using the tables right, we can make sure electrical setups are safe and work well. This is true for homes, businesses, or big buildings. For more on recycling PVC used in conduits, check out this guide16.
Practical Applications of Conduit Fill Calculations
Conduit fill calculations are key in creating safe and efficient electrical installs. They ensure safety and optimize setup across various settings. Let’s explore their use in homes, businesses, and factories.
Residential Wiring
For home wiring, getting conduit fill calculations right is vital. They help pick the best conduit size for wiring lights, outlets, and more. Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT) is great for homeowners because it’s light, easy to install, and saves money17. ENT also helps hide wires neatly, which is perfect for modern homes17.
Commercial Installations
In business spaces, these calculations follow safety rules and save space. Conduits like EMT, IMC, and RMC each hold different amounts and types of wires, affecting wiring plans18. EMT, for instance, works well for grounding, while PVC can handle a bunch of cables19. ENT is used to keep wires in order at offices, improving safety and work flow17.

Industrial Settings
Factories have special needs that make conduit fill calculations a must. They ensure guidance from the NEC is followed, including proper grounding18. ENT suits tough factory conditions, protecting against damp and damage17. It’s also chosen for under concrete installs for its strength and reliability17.
Getting the conduit fill calculations spot on is critical for wiring in any setting. They keep installations safe, efficient, and in order. Following guidelines and selecting the right conduits makes sure electrical systems work well and meet safety standards.
Electrical Wire Sizing
Knowing how to size electrical wires right is key for safe, effective electrical systems. The right wire size is important for how well and safely the system works.
Basics of Wire Sizing
Choosing the right wire gauge helps electricity move safely and well. It’s based on how much electricity is used, how far it travels, and voltage drop. For example, 6-gauge THHN/THWN wires need at least 3/4-inch or 1-inch conduits for three to five wires. This can change with local rules20. Also, a 6/3 wire’s cross-section is about 8.3 square millimeters. This affects which conduit size is picked21.
Factors Influencing Wire Size
Several things matter when picking the right wire size. These include:
- Load Requirements: The key is how much current the wire needs to carry. Bigger loads mean bigger wires to avoid too much heat.
- Voltage Drop: Long wires can lose voltage. Bigger wires help keep the voltage steady over distance.
- Conduit Fill: The NEC says conduit can’t be over 40% full21. This rule helps wires stay cool and safe during setup.
Choosing the Right Wire Size
It’s crucial to pick the right wire size for safety and function. For cables like 6/3 NM-B or 6/3 UF-B, a 1-inch conduit is usually needed20. Going bigger, like 1-1/2 inches or 2 inches, makes putting wires in easier and allows for later changes21. For 6/3 wires, 3/4-inch PVC conduits are often used, while 1-inch is suggested for aluminum and steel conduits21.
Conduit Sizing for Wire Gauge
It’s key to know how to properly size conduit for wire gauge for safety in electrical setups. This means figuring out the right conduit size for the wire gauge you’re using. By doing so, you follow safety standards and ensure everything works well.
The Relationship Between Conduit and Wire Size
The link between conduit and wire size is vital. Getting the right match helps avoid risks like overheating and damage to wires. The NEC sets rules to keep electrical systems safe and working well, like not filling conduit more than 40% with wires22. improvements in how conduits are made, such as adding coatings that resist corrosion and making them lighter, help a lot23.
Calculating the Right Conduit Size
To calculate the right conduit size, start with the wire gauge and how full the conduit can be. For example, a 1-inch conduit can hold up to three 6-gauge wires, following NEC rules22. Here is what you do next:
- Determine the number of conductors: Figure out how many wires you need to fit. Think about the size of each wire.
- Refer to conduit fill charts: Look at charts to see the max amount of space your wires can take. These charts are based on NEC limits: 53% for one wire, 31% for two, and up to 40% for more23.
- Compare conductor areas with conduit capacity: Make sure the total size of your wires doesn’t go over the conduit’s limit. For example, the space taken by a 6/3 wire is about 8.3 square millimeters22.
- Account for conduit spacing: Keep conduits at least 3 inches apart. Use supports every 4 feet to maintain this spacing23.
By taking these steps and using the right tools, electrical pros can make sure their projects are safe and meet regulations. This approach is essential for any electrical task, no matter the setting.
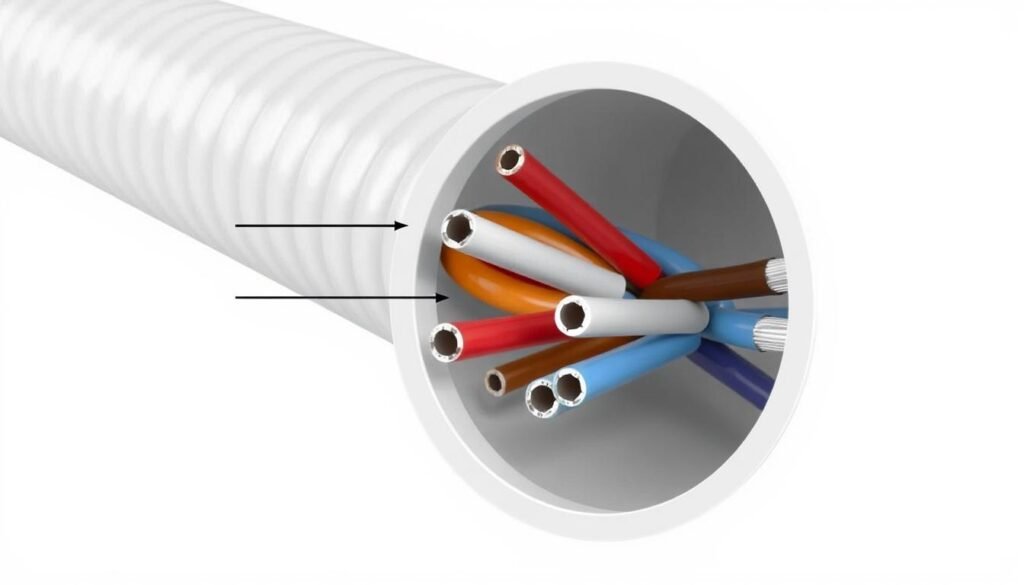
Wire Conduit Compatibility
The idea of matching wires with the right conduit is key for safe and effective electrical setups. It’s about picking the proper conduit type and size for the wires, which ensures they’re well-protected and up to code. This step helps avoid dangers like overheating and electrical mishaps. Let’s explore how to ensure this compatibility, tackle common problems, and follow the best practices during installation.
Ensuring Compatibility
Matching wires and conduits correctly is essential. The National Electrical Code sets a max fill of 40% for conduits with three or more wires. This limit helps avoid too much heat and makes wire pulling easier24. For example, a 6/3 wire setup usually needs at least a 3/4-inch conduit. But, choosing a 1-inch conduit provides better cooling24. Also, conduits come in various materials like PVC and aluminum, each offering different benefits for lasting and safe installations25.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Fixing conduit problems often involves spotting mismatches that could cause overheating or damage to the wires. A typical issue is choosing a conduit that’s too small, which complicates wire installation and increases heat24. For example, 6/3 NM-B cables generally need at least a 1-inch conduit. And for certain cables, like SE or MC, a larger 1-1/4 inch conduit is usually necessary due to their size24. It’s also vital to follow the NEC and local codes to guarantee the safety and functionality of your electrical setups25.
Best Practices for Installation
Following best practices for conduit installation is crucial for a safe and reliable electrical system. Begin by choosing a conduit that can hold all your wires without going over the NEC’s 40% fill limit24. Flexible conduits, like LFMC and Plastic Flex, are great for tight spots. They adapt well to different settings25.
Opt for conduits that resist heat and water, matching them with suitable wires like THHN and THWN, to boost installation safety and compatibility. Finally, consider the needs of your industry. For instance, food and beverage areas may require special food-grade conduits to meet high cleanliness standards25.
Conclusion
It’s very important to know how to fill and size wires correctly for electrical work. We’ve looked closely at how to calculate conduit fill. We also talked about the rules from the National Electrical Code (NEC). It’s key to keep fills at 40% for new setups and not go over 60% for additions. This helps avoid damage to Ethernet and other low-voltage cables26.
Knowing how conduit size and wire gauge connect helps make installations safe and efficient. This is really important in places where the environment changes or you might add more wires later27. In places like stores or offices, using strong metal conduits, like EMT and IMC, is better than using ones made of plastic26.
When wiring, picking the right materials and conduit sizes is crucial. This is true no matter if you’re working on homes, businesses, or big factories. Following the rules helps make sure everything fits right and works without problems27. By doing this, we make electrical systems that are safe, work well, and last a long time.



