Make some changes to the world environment
-
Building 3, Wanyang Innovation City, Langxia Street, Yuyao City, Zhejiang Province

Decomposition Rate of Plastic Explained
Have you ever wondered how long it takes for plastic to decompose? Plastic pollution is a big problem for our planet. Different types of plastics, like HDPE and PET, don’t break down easily. This makes the growth of plastic waste in landfills and oceans a serious issue. It’s important to know how this impacts the environment.
Research tells us that plastics take a very long time to break down. For example, plastic bags can take around 20 years, while water bottles might last for 450 years1. Even things we use every day, like coffee cups with plastic lining and plastic rings from soda cans, take 30 to 400 years to decompose1. Toothbrushes and disposable diapers are even worse, lasting up to 500 years1. This shows why we need to recycle and manage our waste better. You can find out about recycling here.
Many people don’t know that cigarette butts also take about 5 years to break down1. Understanding how long different plastics last can help us reduce their environmental harm. It supports the need for sustainable actions.
Key Takeaways
- HDPE plastic bags take around 20 years to decompose, a lengthier timeline than most organic materials2.
- Plastic water bottles can persist for approximately 450 years, causing long-term environmental damage2.
- Disposable diapers and toothbrushes can take about 500 years to decompose1.
- Soda can rings are another long-lasting plastic, taking up to 400 years to break down1.
- Recycling is essential in mitigating the adverse effects of prolonged plastic decomposition; discover how here.
The Plastic Degradation Process
The way plastic waste breaks down is complicated. It’s affected by the environment, its chemical makeup, and the kind of plastic. Understanding this process is crucial for tackling the problem of global plastic waste.
What is Plastic Degradation?
Plastic degradation is when big polymer chains turn into smaller pieces due to environmental forces. This can take weeks to centuries. It depends on what the plastic is made of and where it is. For instance, PET plastic bottles might take 450 years to decompose. They can even take up to 1000 years to fully break down into tiny microplastics. These microplastics are bad for the environment.
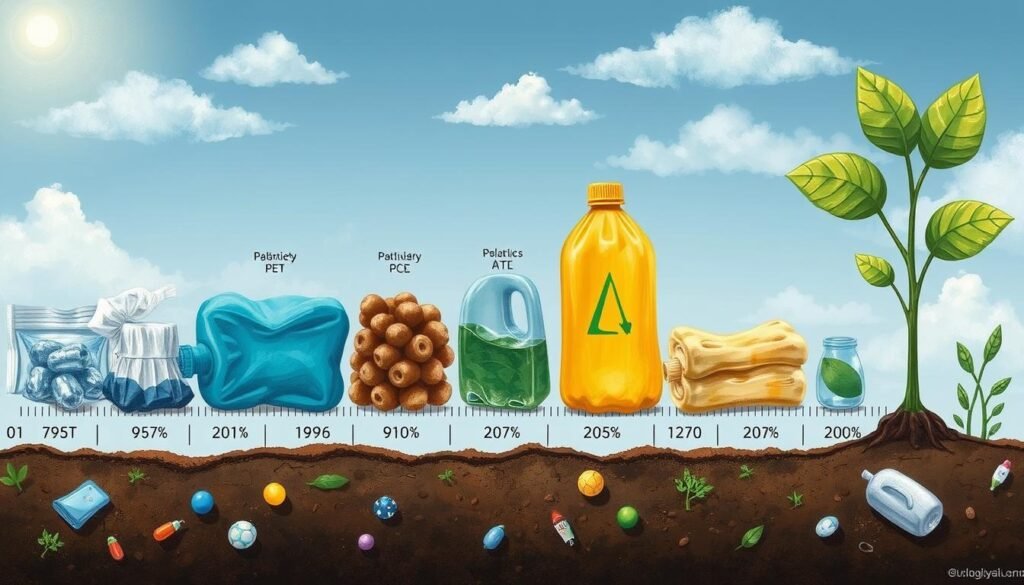
Types of Plastic and Their Decomposition Rates
Different plastics break down at different speeds. Here are some examples:
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): Common in bottles, decomposes in 450 years3.
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): Found in grocery bags, takes 10 to 20 years to decompose3.
- Plastic Straws: It takes about 200 years3.
- Disposable Diapers: They take roughly 500 years3.
- Styrofoam: Also around 500 years3.
- Fishing Line: Breaks down in about 600 years3.
These examples highlight how varied the decomposition rates of plastics can be.
| Type of Plastic | Decomposition Duration |
|---|---|
| PET Bottles | 450 to 1000 years3 |
| HDPE Bags | 10 to 20 years3 |
| Plastic Straws | 200 years3 |
| Disposable Diapers | 500 years3 |
| Styrofoam | 500 years3 |
| Fishing Line | 600 years3 |
Factors Affecting Plastic Decomposition
Many things can change how fast plastic breaks down. They include:
- Sunlight: UV rays speed up the breaking of chemical bonds in plastic.
- Temperature: Warmer temperatures can make plastics degrade faster.
- Microbial Action: Some microbes can help break down certain plastics. But many plastics don’t decompose because of microbes.
- Environmental Conditions: Wetness and wear and tear also affect how fast plastics break down. This is especially true in the ocean, where conditions change a lot.
Getting to know these factors helps us understand how long plastics last. It also shows us how to lessen their impact on the environment by managing waste better.
Plastic Decomposition Timeline
How long plastic takes to break down can vary a lot. For example, plastic bags might take up to 20 years to decompose, while plastic bottles can last up to 500 years. Sadly, only about 30% of these bottles are recycled4. Americans use around 365 plastic bags each, per year, adding greatly to this problem5. Cigarette butts also add to the issue, taking about 10 years to break down4. Plus, it takes 1,000 years for a plastic bag to degrade in a landfill. They break down into microplastics that stick around in our environment5.
Understanding the decomposition of plastic and its impact is key for teaching the public and for making policies. Despite efforts to reduce plastic use, the world still uses 5 trillion plastic bags every year. Many of these end up in places they shouldn’t, like landfills and oceans. Here, they can take hundreds of years to degrade5. And while there are biodegradable options, like certain t-shirts that can take 20 to 200 years to break down, they still present big challenges4. Each year, tons of plastic, including water bottles and wrappers, go into our oceans6.
Different materials take different times to decompose. For instance, paper towels might take 2-4 weeks, but leather can take up to 50 years4. This shows why we need special recycling and waste strategies for different types of plastic waste.
Photos show the serious impacts of plastic waste globally. In both waterways and cities, the lasting presence of plastic shows why we need better waste management solutions in images of plastic pollution4.
Plastic Waste Lifespan in Ocean Environments
Plastic pollution in the ocean is a big problem because plastics last a long time. Cooler temperatures and less sunlight help these plastics last longer in water. This is bad for ocean life.
Impact of Saltwater on Plastic
Saltwater breaks down plastics into tiny pieces called microplastics. These microplastics come from things like clothes and fishing nets. They make ocean pollution worse7.
Most ocean plastic comes from land. Plastic bags take 10 to 20 years to break down in water7. PET plastic bottles can take up to 450 years to decompose. Fishing gear can last up to 600 years. This shows why we need to work hard to reduce plastic waste.

Plastic Pollution and Marine Wildlife
Plastic waste is very harmful to sea animals. Stuff like straws and bags can trap animals or be eaten by them. For example, sea turtles can eat plastic bags thinking they are jellyfish. This can block their stomachs and be deadly8.
Old fishing nets also trap and hurt sea creatures. This is bad for marine life and the diversity of the ocean. Eating plastic hurts animals inside, makes it hard for them to eat, and brings toxins into the food chain. We must tackle this issue to keep the ocean healthy.
Innovative ideas for recycling, like those in PVC plastic recycling, are key to fighting plastic pollution. This helps protect our oceans8.
How Long Does It Take for Plastic to Decompose
The question of how long does it take for plastic to decompose depends on the type of plastic and where it is. Plastic waste can take from several decades to hundreds of years to break down. This range is due to different factors.

For example, plastic bags used for groceries can decompose in 10 to 20 years. Plastic straws, however, need 100 to 500 years. Items like plastic bottles and diapers can take up to 450 years to decompose9. This shows the huge environmental challenge they pose.
Studies say that by 2050, there could be more plastic in the sea than fish. And nearly all seabirds might have eaten plastic9. This fact highlights why it’s crucial to understand how long plastic waste lasts. Generally, it can take hundreds to thousands of years for plastic to fully decompose, showing its lasting impact on the environment10.
But, in warm ocean waters, some plastics can break down faster. Materials like polyethylene and polypropylene may degrade within a year11. The environment plays a big role in how fast plastic waste can decompose.
To grasp these decomposition times better, look at this detailed table showing the lifespan of various plastic items:
| Type of Plastic Item | Decomposition Time (Years) |
|---|---|
| Plastic Grocery Bags | 10-20 |
| Plastic Straws | 100-500 |
| Plastic Bottles | 450 |
| Plastic Diapers | 450 |
| Plastic Sanitary Pads | 450-1000 |
| Styrofoam Cups | 50 |
| Plastic Sandwich Bags | Up to 1000 |
| Fishing Lines (in ocean) | 600 |
| Polylactic Acid (PLA) | 47-90 days |
The long life of plastic in various environments calls for sustainable handling and alternative materials. Through proper disposal and biodegradable plastic innovations, we can lessen the harm from long decomposing plastics91011. Knowing how long plastic lasts helps us find better ways to manage plastic waste.
Plastic Biodegradation Duration in Landfills
In landfills, plastic takes a very long time to break down. This slow process is because of limited air that hinders microbes. These microbes are crucial for breaking plastic down. For example, plastic-coated paper milk cartons might take around five years to decompose. Plastic bags, however, could take up to 500 years or more12.
Influence of Landfill Conditions
Conditions in landfills, like how moist they are or their design, majorly affect how fast plastics degrade. Take vegetables, they can rot in just five days to a month if conditions are right in a landfill12. But plastics are tough. They don’t break down easily, adding greatly to the plastic waste issue13.
Comparing Decomposition in Landfills vs. Compost Piles
Compost piles break down organic materials faster than landfills. For instance, paper turns into compost in two to five months, and cotton T-shirts in about six months. But landfills can’t do much to speed up breaking down plastics like PET, LDPE, and HDPE. These plastics make up a big chunk of plastic waste1213. This shows how tough plastics are against decay. It highlights the importance of recycling and using things more than once to lessen plastic’s harm to our planet.
Environmental Impact of Plastic Disposal
Plastic waste greatly harms our planet, causing big problems for nature. Since the 1950s, we’ve made about 8.3 billion tons of plastic. Sadly, 80% of this has ended up in places it shouldn’t be, like landfills or the ocean14. This leads to serious issues for our environment.
Plastic stays around for a long time, which isn’t good for the planet. For example, plastic bags need around 20 years to break down14. Takeaway coffee cups are even worse, taking 30 years because of their plastic lining15. This slow breakdown means more and more plastic piles up.

Oceans suffer a lot from plastic trash. Each year, Australia alone sees 130,000 tonnes of plastic end up in its waters15. This trash hurts sea life and ecosystems, causing long-term damage. Things like plastic rings might take 400 years to go away1514. Even plastic straws can stick around for 200 years in the sea14.
Land is not safe from plastic harm either. Products like plastic bottles and coffee cups can last up to 450 years1514. Disposable diapers add to the problem, taking 500 years to break down. This threatens our soil and water1514.
Some everyday items, like coffee pods and plastic toothbrushes, also last 500 years1514. They release dangerous gases and pollute our water as they slowly decompose. We need to recycle more and find biodegradable options fast.
In Australia, we make nearly 3 million tonnes of plastic a year but recycle less than 12%15. Worldwide, only 10% of plastic gets recycled, says the Environmental Protection Agency14. We must do better at recycling and managing plastic waste to protect our planet.
Plastic Recycling Timeline and Its Benefits
It’s important to understand the plastic recycling timeline and its benefits to tackle plastic waste worldwide. Since the 1950s, people have made 8.3 billion metric tonnes of plastic. Sadly, 6.3 billion tonnes were thrown away, showing the urgent need for recycling16. Yet, only 9% of all plastic waste has been recycled, which means there’s a lot of room for improvement16.
The Recycling Process for Different Types of Plastic
Different plastics need different recycling methods, which affects how well recycling works. For example, plastic bottles might take up to 450 years to break down in dumps. That’s why strong recycling efforts are needed17. Meanwhile, biodegradable plastics can break down in just three to six months, making them a better option for the environment16. In the US, 185 places can recycle bioplastics, and the UK has 170. This shows there’s a chance to do more recycling16.
Advantages of Recycling Over Landfill Disposal
Choosing to recycle plastics instead of dumping them in landfills brings many benefits. Recycling reduces the need for new materials and cuts down on waste. For instance, plastic spoons and forks can take centuries to decompose, adding greatly to landfill waste17. Recycling also saves energy, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and lessens reliance on landfills. To better understand how long different materials take to break down, see the information below:
| Material | Decomposition Time |
|---|---|
| Plastic Bottles (PET/HDPE) | 450 – 1,000 years17 |
| Plastic Bags | 10 – 1,000 years17 |
| Plastic Straws/Coffee Lids | Up to 200 years17 |
| Plastic Cutlery | Hundreds of years17 |
| Glass | 1 million years18 |
| Aluminum Cans | 100+ years18 |
| Paper | About 5 months18 |
| Vegetable/Fruit Waste | Weeks to months18 |
We need to speed up our recycling efforts and use better recycling technologies. Focusing on and acting on the advantages of recycling plastic will greatly lessen the harm to our planet and support sustainable growth.
Plastic Decomposition Factors: Sunlight, Temperature, and More
Sunlight, especially UV rays, plays a key role in breaking down plastic. This process, called photodegradation, makes plastic fall apart into smaller pieces. When it gets hotter, this breakdown speeds up. But, this process also leads to tiny particles called microplastics. These small pieces can stick around for a long time, hurting our planet.
Heat is another key factor in how fast plastic decomposes. Warmer temps boost the activity of microbes that eat away at plastic. But not all places are warm enough for this to happen fast. For example, plastic bags might take up to 20 years to break down. Plastic bottles and disposable diapers could last for 450 to 500 years1920.
Oxygen level is important too for plastic to decompose. In places with lots of oxygen, some microorganisms can break down plastics faster. Yet, in places without much oxygen, like deep in landfills, plastics take longer to decompose. The way sunlight, microbes, temperature, and oxygen work together shows how complex plastic breakdown is21.
We need good waste management plans to lessen plastic’s harm. These should focus on using less plastic and better recycling. Handling the leftovers from decomposition helps us fight plastic pollution and protect nature. By doing this, we also cut down on harmful gas emissions and pollution from trash disposal2119.
Conclusion
Plastic takes a long time to break down, showing our current way of throwing stuff away won’t work long-term. Knowing how long plastic stays around helps us see why we must manage waste better and faster.
For example, plastic bags can last over 20 years and bottles up to 450 years, seriously harming our planet2223. Most plastics found deep in the ocean are polyethylene, making up 80% of what’s found24. Also, wet wipes block our sewers for around 100 years, pushing us to find better options and improve how we handle trash22.
Companies like Birch Plastics are vital in making plastic disposal better by using innovative, green tech. By creating high-quality LDPE pellets, they make plastics that are both more efficient to use and easier to recycle, reducing harm to the environment.
To truly care for our planet, we need to do several things all at once. This includes better trash handling, teaching people about the issue, and coming up with new ways to make and get rid of plastic. By working together and using new tech, we can tackle the problem of plastic lasting too long and help our environment.



