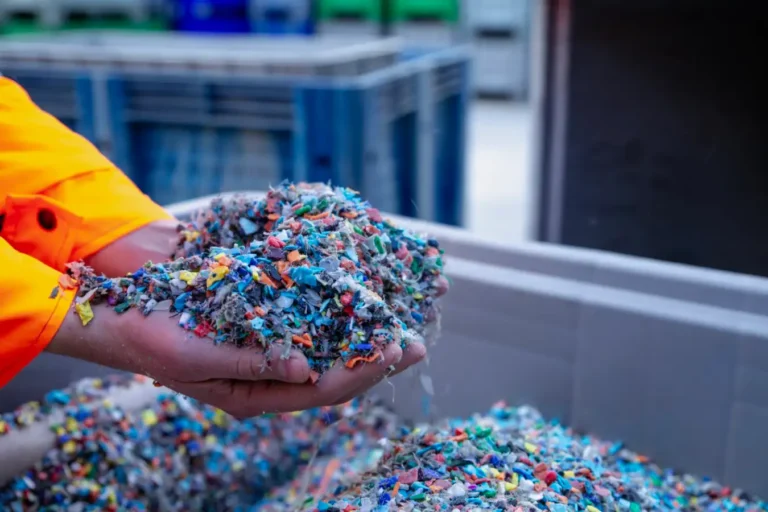
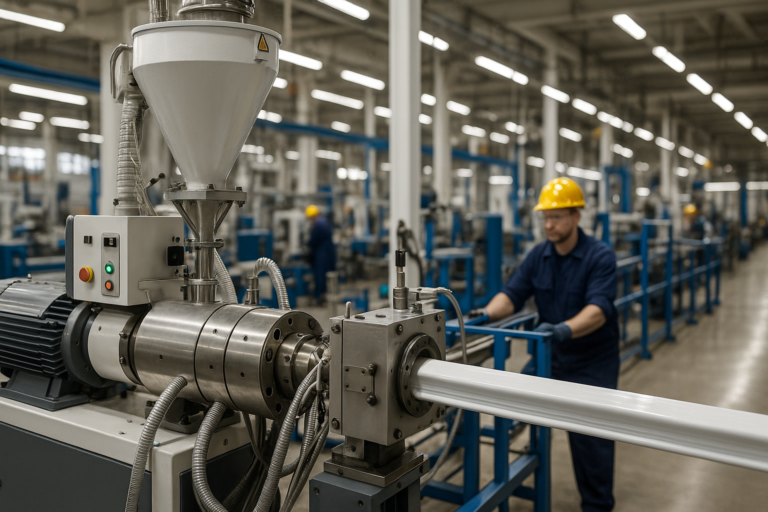
Nehmen Sie einige Änderungen an der Weltumgebung vor
-
Gebäude 3, Wanyang Innovation City, Langxia Street, Yuyao City, Provinz Zhejiang

Vom Granulat zum Produkt: Der Prozess der Kunststoffextrusion im Überblick
Lernen Sie den Prozess der Kunststoffextrusion von Anfang bis Ende kennen und erfahren Sie mehr über die Komponenten, Arten und Vorteile einer effektiven Fertigung.
Die Grundlagen der Kunststoffextrusion: Vom Rohstoff zum fertigen Produkt
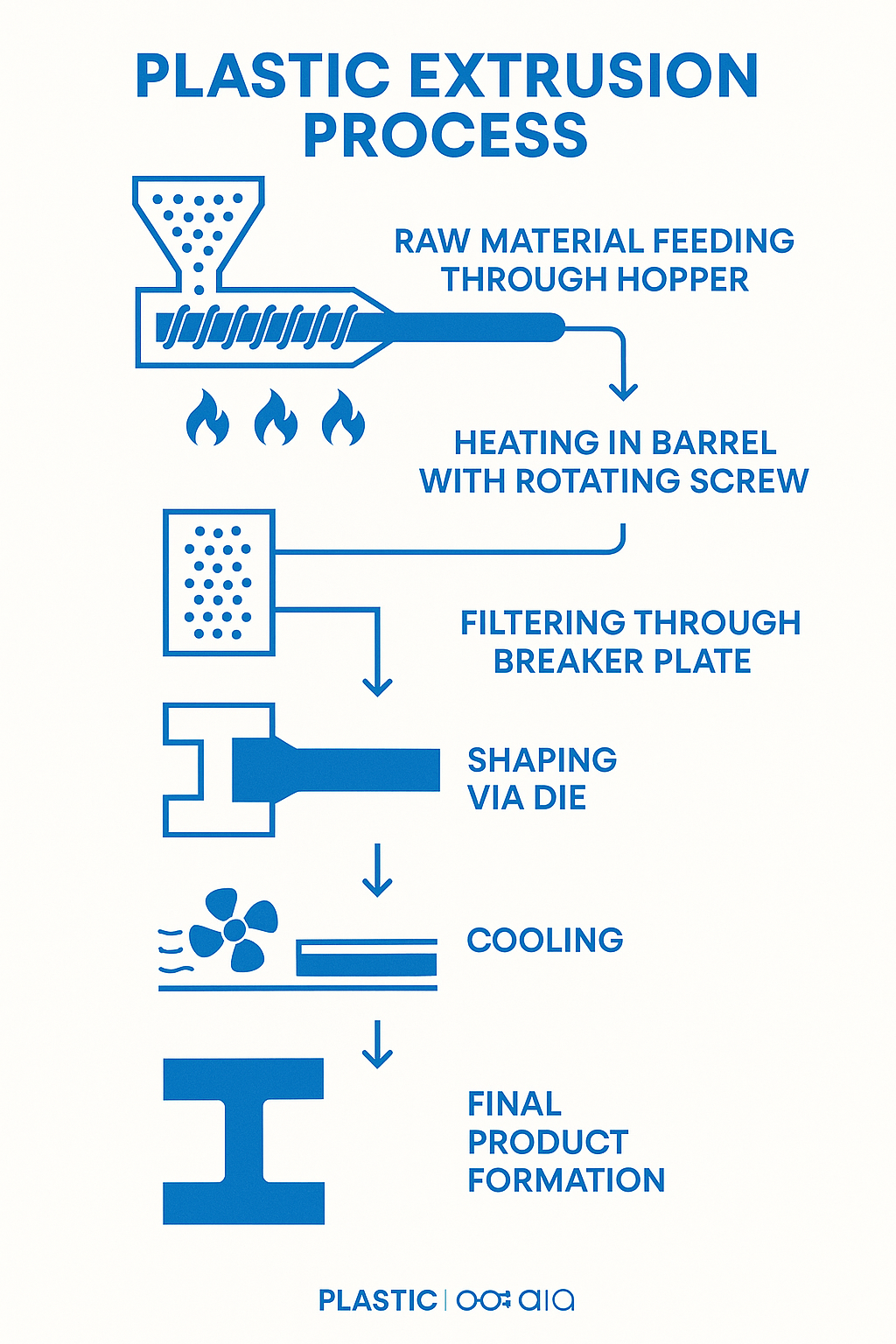
Die Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren ist ein kontinuierliches Herstellungsverfahren, bei dem Kunststoffrohmaterialien in Produkte mit einem gleichmäßigen Querschnitt umgewandelt werden. Wenn Sie wissen möchten, wie die Kunststoffextrusion funktioniert, finden Sie hier einen kurzen Überblick:
| Kunststoff-Extrusionsverfahren | Beschreibung |
|---|---|
| Schritt 1: Fütterung | Rohes Kunststoffgranulat wird in einen Trichter gefüllt und gelangt in den Extruder |
| Schritt 2: Schmelzen | Das Material durchläuft einen beheizten Zylinder, wo es schmilzt (200-275°C) |
| Schritt 3: Komprimierung | Eine rotierende Schnecke (bis zu 120 U/min) komprimiert und homogenisiert den geschmolzenen Kunststoff |
| Schritt 4: Filterung | Siebe und Brecherplatten entfernen Verunreinigungen und erzeugen Gegendruck |
| Schritt 5: Formgebung | Geschmolzener Kunststoff wird durch eine Form gepresst, um das gewünschte Profil zu erzeugen |
| Schritt 6: Kühlung | Das extrudierte Produkt wird abgekühlt, um seine Form zu verfestigen |
| Schritt 7: Fertigstellung | Das Produkt wird auf Länge geschnitten oder auf Spulen aufgewickelt |
Die Kunststoffextrusion ist seit über einem Jahrhundert ein Eckpfeiler der Fertigung und hat sich zu einem der effizientesten Verfahren zur Herstellung von kontinuierlichen Kunststoffprodukten entwickelt. Die Schönheit dieses Verfahrens liegt in seiner Fähigkeit, alles von einfachen Rohren und Schläuchen bis hin zu komplexen Profilen mit gleichbleibender Qualität in großen Mengen herzustellen.
"Die Kunststoffextrusion ist ein hochvolumiger Fertigungsprozess, bei dem präzise mechanische und thermische Kontrollsysteme zum Einsatz kommen", so Branchenexperten. Diese Präzision ermöglicht es den Herstellern, konsistente Produkte zu produzieren und gleichzeitig die Effizienz zu erhalten.
Für umweltbewusste Produktionsmanager ist das Verständnis dieses Prozesses von entscheidender Bedeutung. Es bietet nicht nur die Möglichkeit, recycelte Materialien zu verwenden, sondern die Optimierung des Extrusionsprozesses kann auch den Abfall und den Energieverbrauch erheblich reduzieren - kritische Faktoren im heutigen, auf Nachhaltigkeit ausgerichteten Produktionsumfeld.
Unter JianTai Plastic Machinery Company haben wir gesehen, wie die Beherrschung des Extrusionsprozesses den Herstellern hilft, ihren ökologischen Fußabdruck zu verringern und gleichzeitig eine hochwertige Produktion zu gewährleisten. Das Verfahren verwandelt Kunststoffabfälle in wertvolle neue Produkte und unterstützt damit die Kreislaufwirtschaft, die für die Zukunft unseres Planeten so wichtig ist.
Was ist das Verfahren der Kunststoffextrusion?
Die Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren ist wie eine hochentwickelte Version des Drückens von Play-Doh durch einen Former - nur dass wir statt mit Play-Doh mit thermoplastischen Materialien bei hohen Temperaturen und hohem Druck arbeiten. Bei diesem großvolumigen Herstellungsverfahren werden Kunststoffgranulate in kontinuierliche Produkte mit gleichmäßigen Querschnitten umgewandelt.
Stell dir vor, du drückst Zahnpasta aus einer Tube. Die Zahnpasta hat immer die gleiche Form wie die Tubenöffnung. Bei der Kunststoffextrusion wird geschmolzener Kunststoff zu unserer "Zahnpasta" und eine präzise konstruierte Düse dient als "Tubenöffnung", die das Material zu allem Möglichen formt, von einfachen Rohren bis zu komplexen Fensterrahmen.
Das Besondere an der Extrusion ist die Fähigkeit, Produkte mit exakt demselben Profil herzustellen, Fuß für Fuß, Kilometer für Kilometer. Ganz gleich, ob Sie Hunderte oder Tausende von Metern Produkt benötigen, Sie erhalten durchweg eine bemerkenswerte Konsistenz.
"Nach ihrer Fertigstellung nehmen Produkte aus Kunststoff viele verschiedene Formen an, aber sie beginnen alle am gleichen Ort und aus dem gleichen Rohstoff - Harz", erklären die Branchenexperten von Plastrading.com. Dieses grundlegende Prinzip verleiht der Extrusion ihre unglaubliche Vielseitigkeit bei der Herstellung.
Während der KunststoffextrusionsverfahrenBei diesem Verfahren werden Rohstoffe in Form von Pellets, Perlen oder Pulver (allgemein als "Harz" bezeichnet) durch sorgfältig kontrollierte Hitze und Druck in fertige Produkte verwandelt. Bei diesem Verfahren können Drücke von über 34 MPa (5.000 psi) erzeugt werden - das ist die Kraft, die erforderlich ist, um geschmolzenen Kunststoff mit höchster Präzision durch die Düse zu drücken.
Die Grundlagen der Kunststoffextrusion
Im Kern geht es darum, die Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren hängt von thermoplastischen Harzen ab - Materialien mit einer Superkraft: Sie können wiederholt geschmolzen und verfestigt werden, ohne dass es zu einem nennenswerten Abbau kommt. Diese bemerkenswerte Eigenschaft macht die Kunststoffextrusion nicht nur effizient, sondern auch umweltfreundlich, da Materialreste oft wiederverwertet werden können, anstatt sie zu verschwenden.
Die Reise beginnt, wenn Kunststoffgranulat durch einen Einfülltrichter in den Extruder fällt. Während diese winzigen Teile durch den Zylinder wandern, treffen sie auf einen Temperaturgradienten, der je nach verarbeitetem Kunststoff typischerweise zwischen 200 und 275 °C liegt.
Und hier wird es interessant: Während externe Heizungen den Zylinder erwärmen, stammen etwa 70-80% der Wärme aus der mechanischen Reibung, die durch die rotierende Schnecke erzeugt wird! In Hochgeschwindigkeits-Produktionslinien schalten die Bediener die Heizungen manchmal sogar ganz aus - allein die Reibung sorgt für perfekte Schmelztemperaturen.
Der Schmelzvorgang erfolgt schrittweise und nicht auf einmal. Zunächst bildet sich ein dünner Film aus geschmolzenem Kunststoff an der Zylinderwand, der sich dann langsam ausdehnt, bis das gesamte Material die richtige Konsistenz erreicht hat. Dieses kontrollierte, progressive Schmelzen ist entscheidend für die Produktqualität und verhindert Fehler, die das Endprodukt beeinträchtigen könnten.
Sobald der Kunststoff vollständig geschmolzen ist, fließt er durch eine Düse, die ihn in das gewünschte Profil formt. Das neu geformte Extrudat muss dann schnell erstarren, was je nach Produkt durch Kühlsysteme wie Luftgebläse, Wasserbäder oder spezielle Kühlwalzen geschieht.
Wie es ein Veteran der Kunststoffindustrie so schön ausdrückt: "Ob Sie es glauben oder nicht, dieser 'Schmelztiegel' ist eigentlich ein Rohr!" Diese einfache Beobachtung macht deutlich, wie die scheinbar komplexe Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren beruht auf den einfachen Prinzipien von Wärme, Druck und Fluss, um unzählige Produkte herzustellen, die wir täglich verwenden.
Bei JianTai haben wir diesen Prozess so verfeinert, dass er hervorragend mit recycelten Materialien funktioniert und Herstellern hilft, hochwertige Produkte herzustellen und gleichzeitig die Umweltbelastung zu reduzieren - eine Win-Win-Situation für Unternehmen und Umwelt.
Hauptkomponenten einer Kunststoffextrusionsmaschine
Haben Sie sich schon einmal gefragt, was in diesen riesigen Maschinen steckt, die winzige Kunststoffgranulate in Rohre, Profile und unzählige andere Produkte verwandeln? Lassen Sie uns eine Reise durch das Herz der Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren indem wir die Schlüsselkomponenten erforschen, die die Magie möglich machen.
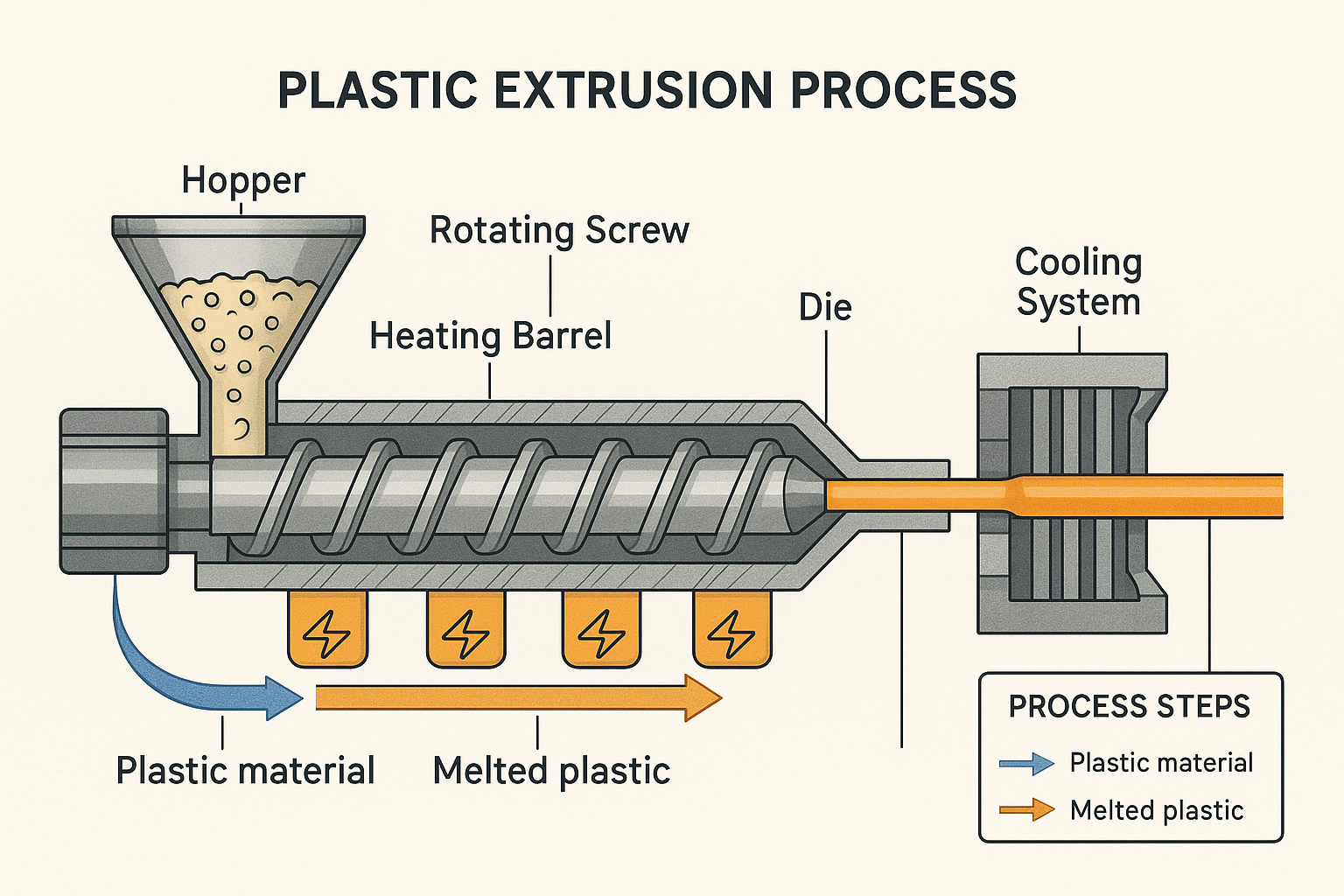
Stellen Sie sich einen Extruder als ein sorgfältig orchestriertes System vor, in dem jedes Teil eine entscheidende Rolle im Veränderungsprozess spielt. Bei JianTai haben wir Jahre damit verbracht, diese Komponenten zu perfektionieren, damit sie harmonisch zusammenarbeiten.
Die Reise beginnt an der Einlauftrichter - ist im Wesentlichen ein großer Trichter, der die rohen Kunststoffgranulate aufnimmt, bevor sie in die Maschine gelangen. Das Design des Trichters mag zwar einfach erscheinen, ist aber in Wirklichkeit ziemlich ausgeklügelt. Wir bevorzugen runde Trichter gegenüber quadratischen Trichtern, weil sie verhindern, dass das Material bei unterschiedlichen Partikelgrößen stecken bleibt oder "Brücken" bildet.
Von dort aus wird der Kunststoff durch die Futterkehleder den Trichter mit dem Zylinder verbindet. Dieser Bereich muss sorgfältig gekühlt werden, um ein vorzeitiges Schmelzen zu verhindern, das zu lästigen Verstopfungen führen könnte - stellen Sie sich vor, Sie versuchen, Zahnpasta zurück in die Tube zu drücken, und Sie werden die Herausforderung verstehen!
Die Fass ist der Ort, an dem es richtig heiß wird. Das Gehäuse der Schnecke ist von Heizelementen umgeben und in mehrere Temperaturzonen unterteilt, die den Kunststoff nach und nach erwärmen, während er sich vorwärts bewegt. Jede Zone wird von hochentwickelten PID-Reglern unabhängig gesteuert, sodass wir das perfekte Temperaturprofil für verschiedene Materialien erstellen können.
Das Herzstück des Systems ist die Schraube - vielleicht die kritischste Komponente in der gesamten Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren. Dieses präzisionsgefertigte Teil dreht sich im Zylinder mit nur einem Hauch von Spiel (normalerweise etwa 0,001 des Schneckendurchmessers). Durch die Drehung wird der Kunststoff nicht nur vorwärts bewegt, sondern auch komprimiert, geschmolzen und gemischt, um ein gleichmäßiges geschmolzenes Material zu erzeugen.
Rund um das Fass finden Sie die Heizzonen - externe Heizelemente, die mit der von der Schraube erzeugten Reibungswärme zusammenarbeiten. Es ist ein sorgfältiger Balanceakt - zu viel Wärme und der Kunststoff zersetzt sich, zu wenig und er schmilzt nicht richtig.
Wenn sich der geschmolzene Kunststoff dem Ende seiner Reise durch den Zylinder nähert, trifft er auf die Unterbrecherplatte - eine perforierte Metallscheibe, die zwei wichtige Zwecke erfüllt. Erstens erzeugt sie Gegendruck für ein besseres Schmelzen, und zweitens beseitigt sie das "Rotationsgedächtnis" des Kunststoffs. Ohne dieses könnte sich Ihr Endprodukt nach der Extrusion unvorhersehbar verdrehen!
Unmittelbar vor der Unterbrecherplatte befindet sich die Bildschirmpaket - Schichten von Drahtgewebe, die als Filter dienen, um Verunreinigungen oder ungeschmolzene Partikel aufzufangen. Diese Siebe reichen in der Regel von grob bis fein und stellen sicher, dass nur perfekt geschmolzener, sauberer Kunststoff in die Düse gelangt.
Die die ist der Ort, an dem Ihr Produkt Gestalt annimmt. Dieses präzisionsgefertigte Bauteil hat eine Öffnung, die dem Querschnitt Ihres gewünschten Produkts entspricht. Die Konstruktion der Matrize erfordert ein hohes Maß an Fachwissen, da die natürliche Tendenz des Kunststoffs, sich nach dem Austritt aus der Matrize leicht auszudehnen, berücksichtigt werden muss.
Sobald der heiße Kunststoff aus der Form austritt, wird die Kühlsystem übernimmt. Je nach Produkt kann es sich dabei um Wasserbäder, Kühlwalzen oder Luftkühlsysteme handeln. Die richtige Kühlung ist von entscheidender Bedeutung - kühlen Sie zu schnell, besteht die Gefahr des Verziehens, kühlen Sie zu langsam, verlangsamt sich die Produktion.
Endlich, Abzugsgeräte zieht das extrudierte Produkt mit genau kontrollierten Geschwindigkeiten sanft aus der Düse und trägt so zur Bestimmung der endgültigen Abmessungen Ihres Produkts bei.
Die Rolle der Schnecke bei der Kunststoffextrusion
Wenn es eine Komponente gibt, die besondere Aufmerksamkeit in der Kunststoffextrusionsverfahrendann ist es definitiv die Schnecke. Dieses scheinbar einfache Teil ist in Wirklichkeit ein technisches Wunderwerk, das mehrere wichtige Funktionen erfüllt, während sich der Kunststoff durch die Maschine bewegt.
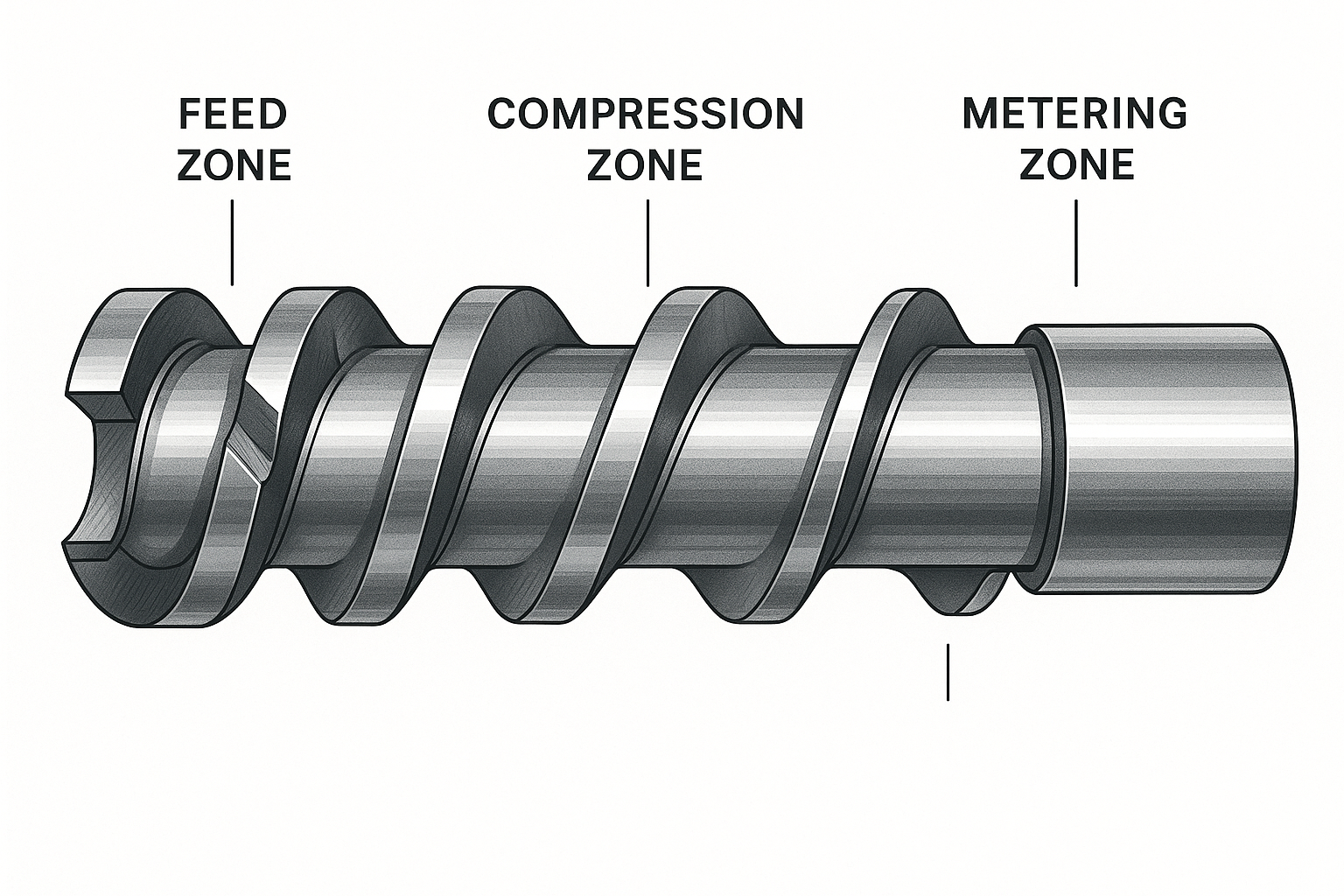
Die Schnecke ist in drei Hauptzonen unterteilt, von denen jede einen bestimmten Zweck erfüllt, um das harte Kunststoffgranulat in eine perfekt gleichmäßige Schmelze zu verwandeln:
Die Futtermittelbereich beginnt die Reise mit tiefen Gängen (den spiralförmigen Rippen an der Schnecke), die das Material effizient aus dem Trichter befördern. Stellen Sie sich diesen Bereich als "Sammelbereich" vor, mit großen Kanaltiefen, die den Materialeinzug maximieren.
Wenn sich der Kunststoff vorwärts bewegt, gelangt er in die Kompressionszone (manchmal auch als Übergangsbereich bezeichnet). Hier wird es interessant: Die Flugtiefe nimmt allmählich ab, wodurch der Kunststoff komprimiert und eingeschlossene Luft herausgedrückt wird. Diese Kompression ist für eine gleichmäßige Schmelze unerlässlich, wobei das Kompressionsverhältnis je nach Material typischerweise zwischen 2:1 und 4:1 liegt.
Schließlich ist die Dosierzone verfügt über flache, gleichmäßige Gänge, die eine gleichmäßige Schmelze und einen stabilen Druck erzeugen, bevor der Kunststoff die Düse erreicht. Diese letzte Zone gewährleistet, dass Ihr Produkt durchgehend eine gleichbleibende Qualität aufweist.
Einige fortschrittliche Schrauben umfassen zusätzliche Spezialzonen. A Dekompressionszone könnte in entlüfteten Schnecken vorhanden sein, die den Druck reduzieren, damit Gase durch eine Entlüftung im Zylinder entweichen können - besonders nützlich bei der Verarbeitung von recycelten Materialien, die Feuchtigkeit oder flüchtige Stoffe enthalten können. Anschließend würde eine Zweite Zählzone um das Material für die Extrusion wieder unter Hochdruck zu setzen.
Die Effektivität einer Schnecke wird häufig anhand ihres L/D-Verhältnisses gemessen, d. h. Länge zu Durchmesser. Das Standardverhältnis liegt in der Regel zwischen 25:1 und 40:1, doch bei Spezialanwendungen können noch höhere Verhältnisse zum besseren Mischen und Schmelzen verwendet werden.
Bei JianTai Plastic Machinery Company haben wir spezielle Schneckenkonstruktionen für die Verarbeitung von recycelten Kunststoffen entwickelt, die im Vergleich zu Neuware oft besondere Herausforderungen darstellen. Unsere Schneckentechnologie mit variablem Durchmesser, gepaart mit Zwangszuführungsmechanismen, gewährleistet eine kontinuierliche, genaue und gleichmäßige Verarbeitung selbst bei gemischten Kunststoffabfällen - und verwandelt die weggeworfenen Verpackungen von gestern in die nützlichen Produkte von morgen.
Möchten Sie tiefer in die Auswahl der perfekten Schraube für Ihre Extrusionsanforderungen eintauchen? Sehen Sie sich unser Ultimativer Leitfaden für die Auswahl von Kunststoffextruderschnecken um Expertenwissen zu erhalten, das zur Optimierung Ihres Produktionsprozesses beitragen kann.
Arten von Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren
Wenn man sich die unglaubliche Vielfalt an Kunststoffprodukten vor Augen führt, die wir täglich verwenden - vom Gartenschlauch bis zur Einkaufstüte -, ist es faszinierend zu erkennen, dass sie alle aus Variationen desselben Herstellungsverfahrens stammen. Die Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren ist bemerkenswert vielseitig, mit spezialisierten Methoden, die auf die Herstellung bestimmter Produkte zugeschnitten sind, aber das gleiche Grundprinzip haben: Kunststoff schmelzen und durch eine geformte Öffnung drücken.
Sehen wir uns die wichtigsten Arten von Extrusionsverfahren an, mit denen Rohkunststoff in die Produkte umgewandelt wird, auf die wir uns jeden Tag verlassen:
Verfahren der Schlauchextrusion
Wenn Sie jemals Ihren Garten bewässert haben oder einen medizinischen Eingriff hatten, haben Sie von der Schlauchextrusion profitiert. Mit diesem Verfahren wird alles hergestellt, von einfachen Trinkhalmen bis hin zu komplexen medizinischen Schläuchen und Industrierohren, die Wasser in unsere Häuser leiten.
Das Besondere an der Schlauchextrusion ist der clevere Einsatz eines Dorns (oder Stifts), der sich im Inneren der Düse befindet. Wenn der geschmolzene Kunststoff durch die Düse fließt, wickelt er sich um diesen Dorn und erzeugt so den hohlen Kern, den wir für Rohre und Schläuche benötigen.
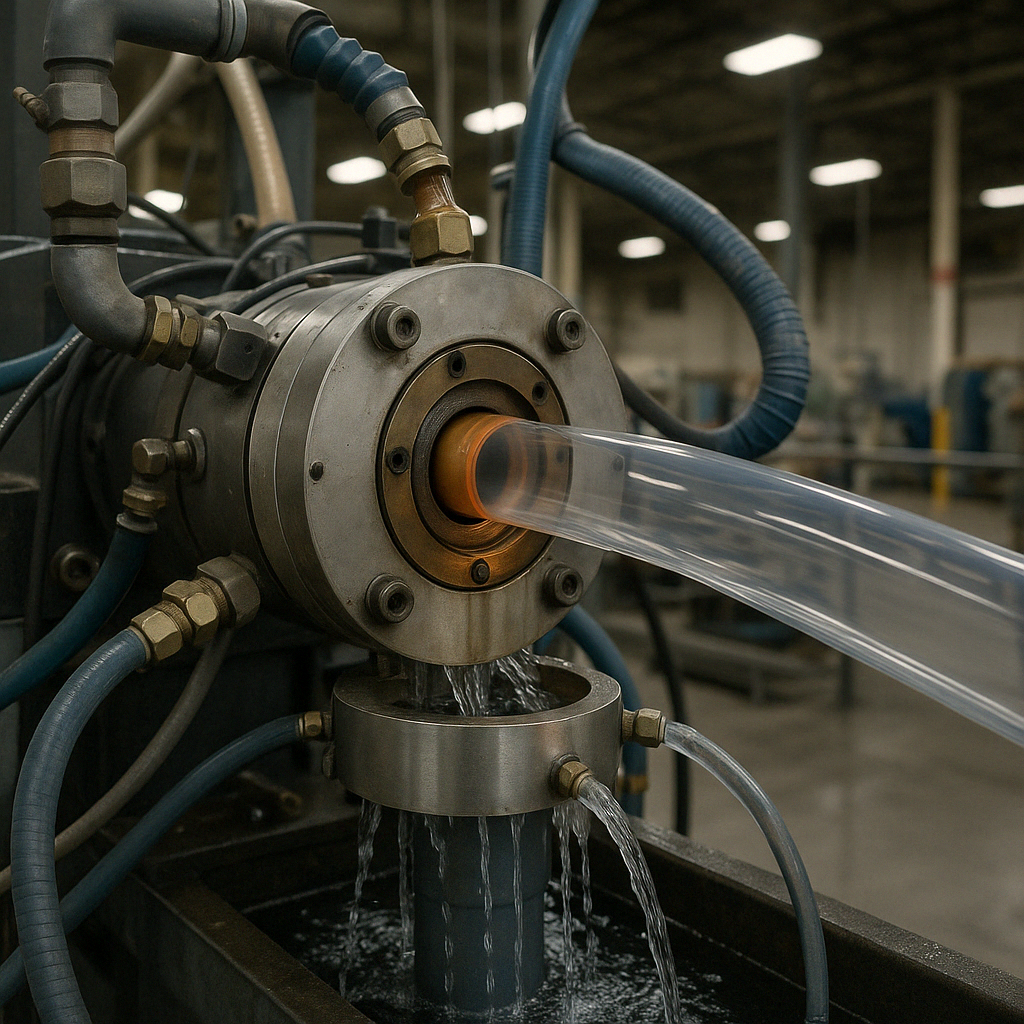

"Bei der Herstellung von Rohren kommt es auf die richtige Balance an", sagte mir einmal ein Produktionsleiter. "Wenn der Druck zu hoch ist, bricht das Rohr zusammen, wenn er zu niedrig ist, hat man unebene Wände. Dieses empfindliche Gleichgewicht erfordert Präzisionsgeräte und Fachwissen.
Nach dem Austritt aus der Matrize durchläuft das neu geformte Rohr eine Kalibrierhülse oder einen Vakuumkalibrator und wird dabei schnell mit Wasser abgekühlt. Bei größeren Rohren verwenden die Hersteller häufig die Vakuumformung, bei der der Kunststoff durch Unterdruck sanft gegen die Kalibrierhülse gezogen wird, um die präzisen Abmessungen zu gewährleisten, die für Anwendungen wie medizinische Geräte oder Automobilkomponenten entscheidend sind.
Bei JianTai haben wir unsere Rohrextrusionsanlagen mit speziellen Kalibrier- und Kühlsystemen ausgestattet, die selbst bei der Verarbeitung von recycelten Materialien - die aufgrund ihrer variablen Schmelzeigenschaften schwierig sein können - die Dimensionsstabilität gewährleisten.
Blasfolienextrusionsverfahren
Die Blasfolienextrusion hat etwas fast Magisches an sich. Bei diesem Verfahren werden die dünnen Kunststofffolien, die für Einkaufstaschen, Lebensmittelverpackungen und Abdeckungen in der Landwirtschaft verwendet werden, durch ein Verfahren hergestellt, das aussieht wie industrielles Blasenblasen.
So funktioniert es: Ein Rohr aus geschmolzenem Kunststoff (ein so genannter "Vorformling") tritt senkrecht aus der Form aus. Dann wird von der Mitte aus Luft in dieses Rohr geblasen, wodurch es sich wie ein Ballon aufbläht und eine sogenannte "Blase" entsteht, die in der Branche als "Bubble" bezeichnet wird. Diese Blase kann sich auf mehr als das Doppelte des ursprünglichen Formdurchmessers ausdehnen!
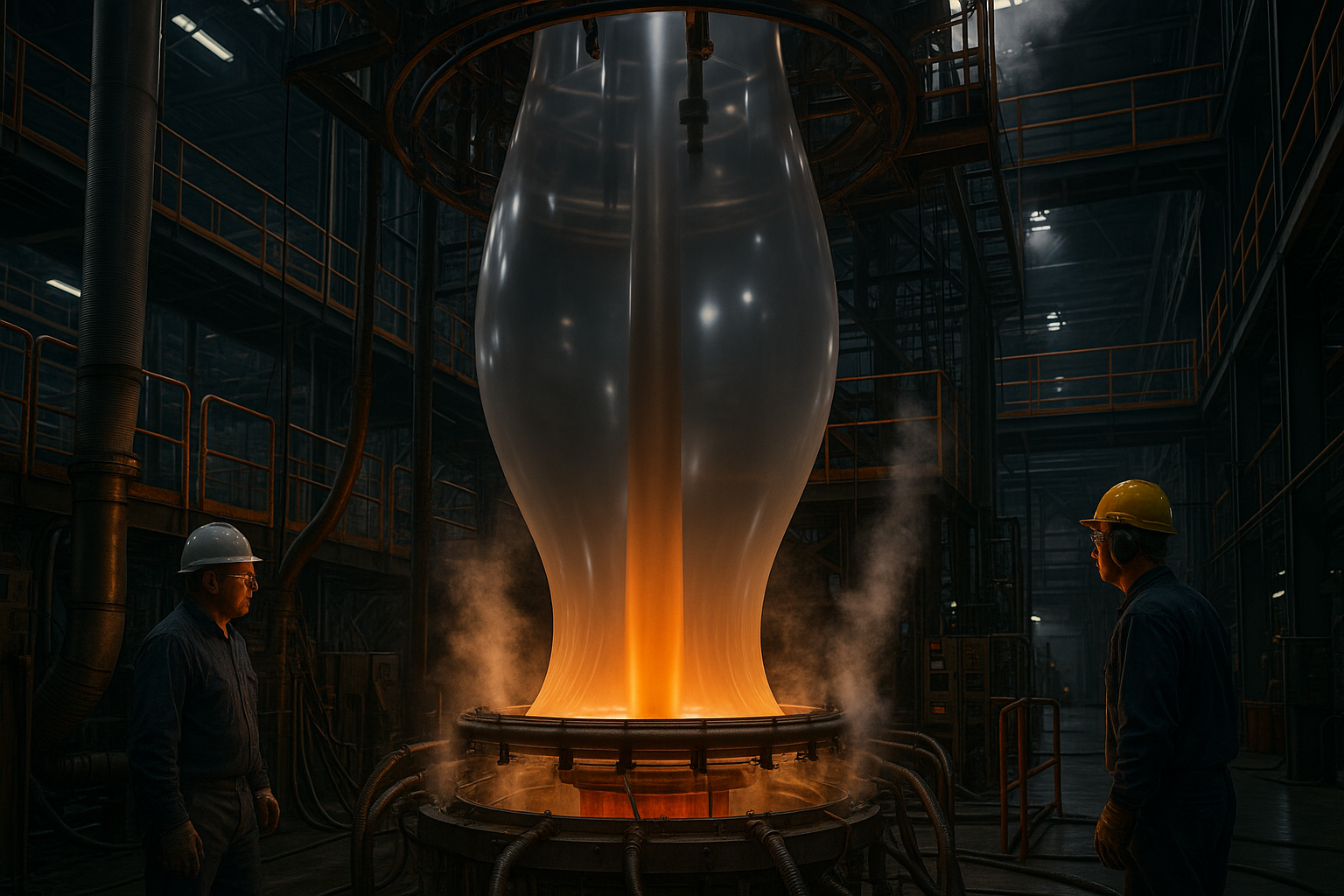

Während diese riesige Blase aufsteigt, kühlt sie ab und verfestigt sich. Am oberen Ende glätten Quetschwalzen den Schlauch zu einer doppellagigen Folie, die auf Rollen aufgewickelt wird. Das Schöne an diesem Verfahren ist, dass die Folie bereits an den Rändern gefaltet ist - perfekt für die Herstellung von Beuteln mit nur wenigen zusätzlichen Schritten.
"Blasfolienextrusion ist wie das Aufblasen eines Luftballons, nur mit wissenschaftlicher Präzision", wie einer unserer Ingenieure zu sagen pflegt. "Jeder Aspekt - Luftdruck, Temperatur, Kühlrate - muss perfekt ausbalanciert sein, um gleichbleibende Ergebnisse zu erzielen."
Moderne Blasfolienanlagen verfügen oft über ausgeklügelte Luftringe für eine gleichmäßige Kühlung und können sogar Mehrschichtfolien durch Coextrusion herstellen, bei der verschiedene Materialien für eine verbesserte Leistung kombiniert werden.
Neben diesen beiden Haupttypen gibt es die Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren umfasst mehrere andere wichtige Varianten:
Folienextrusion produziert dickere Kunststoffplatten, die für Tiefziehprodukte wie Joghurtbecher und Schalenverpackungen verwendet werden. Ummantelungsextrusion überzieht Drähte und Kabel mit einem schützenden Kunststoffüberzug, der von der Haushaltselektronik bis zur Telekommunikationsinfrastruktur unverzichtbar ist.
Co-Extrusion ermöglicht es, mehrere Materialien oder Farben in einem einzigen Durchgang zu kombinieren und Produkte mit Schichten unterschiedlicher Eigenschaften zu schaffen - man denke nur an Lebensmittelverpackungen, die innen und außen unterschiedliche Barriereeigenschaften aufweisen müssen. Profil-Extrusion erstellt komplexe massive Formen wie Fensterrahmen und dekorative Verkleidungen.
Weitere spezialisierte Verfahren sind Extrusionsbeschichtung (Aufbringen dünner Kunststoffschichten auf Materialien wie Papier), Extrusionskaschierung (Verbinden mehrerer Materialien miteinander) und Monofilament-Extrusion (Herstellung von Fasern für Angelschnüre und Industriebürsten).
Kunststoff-Extrusionsmaschine: Recyceln mit Präzision
Die Vielseitigkeit dieser Verfahren erklärt, warum die Extrusion nach wie vor das Herzstück der Kunststoffherstellung ist - und warum wir bei JianTai weiterhin spezielle Anlagen entwickeln, die diese Prozesse effizienter, präziser und umweltfreundlicher machen, insbesondere wenn wir mit recycelten Materialien arbeiten.
Materialien und Anwendungen in der Kunststoffextrusion
Die Welt der Kunststoffextrusion ist bemerkenswert vielseitig, wobei jedes Material seine eigene Persönlichkeit in den Herstellungsprozess einbringt. Wenn ich Fertigungsanlagen besuche, bin ich immer wieder erstaunt, wie die gleichen Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren kann alles herstellen, von Gartenschläuchen bis hin zu medizinischen Schläuchen, indem man einfach das Material, das in den Trichter kommt, ändert.
Stellen Sie sich Thermoplaste als die Chamäleons der Fertigungswelt vor - sie können geschmolzen, geformt, abgekühlt und wieder geschmolzen werden, ohne ihre wesentlichen Eigenschaften zu verlieren. Diese Wiederverwertbarkeit macht sie zu perfekten Partnern für die Extrusion und eine umweltverträgliche Produktion.
Lernen Sie einige der beliebtesten Materialien kennen, die jeden Tag durch Extruder fließen:
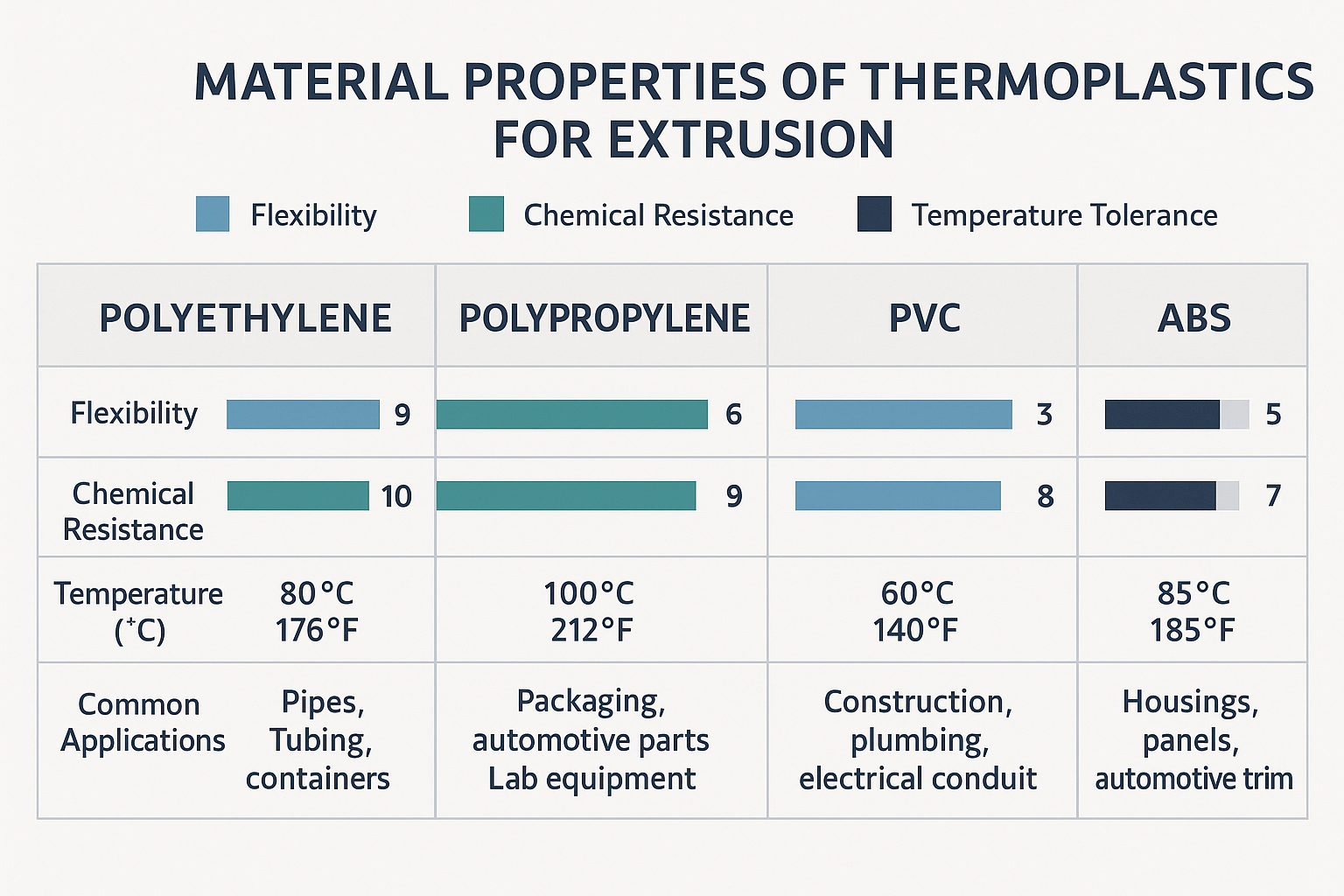
Polyethylen (PE) ist das freundliche, flexible Arbeitspferd der Kunststoffwelt. PE ist in niedriger, hoher und linearer niedriger Dichte erhältlich und macht Ihre Squeeze-Flaschen drückbar und Ihre Einkaufstüten dehnbar. Es ist chemikalienbeständig und kostengünstig und eignet sich daher perfekt für alles, von landwirtschaftlichen Folien bis hin zu Wasserrohren.
Polypropylen (PP) ist der etwas zähere Cousin von Polyethylen. PP ist hitzebeständiger und verfügt über eine ausgezeichnete chemische Beständigkeit, so dass es sich auch in anspruchsvollen Umgebungen bewährt. Deshalb findet man es in allem, von Autoteilen bis hin zu den mikrowellengeeigneten Lebensmittelbehältern in der Küche.
Polyvinylchlorid (PVC) ist vielleicht der bekannteste Name im Bunde. Dieses haltbare, feuerfeste Material hat die Bauindustrie mit seiner starren Form (z. B. Fensterrahmen und Verkleidungen) und seiner flexiblen Version (Gartenschläuche und Isolierung von Stromkabeln) revolutioniert.
Acrylnitril-Butadien-Styrol (ABS) - ist - trotz seines zungenbrecherischen Namens - für seine Zähigkeit und Stoßfestigkeit bekannt. Es verleiht dem Armaturenbrett Ihres Autos diese zufriedenstellende Langlebigkeit und sorgt dafür, dass die Rohrsysteme erheblichen Belastungen standhalten können.
Bei der Materialauswahl geht es nicht nur um die Auswahl eines Kunststofftyps, sondern auch um die Abstimmung bestimmter Eigenschaften auf die Endanwendung. Temperaturbeständigkeit, Flexibilität, Klarheit, UV-Stabilität und sogar Vorschriften zur Lebensmittelsicherheit spielen bei dieser wichtigen Entscheidung eine Rolle.
Wir bei JianTai Plastic Machinery Company haben unsere Anlagen so konzipiert, dass sie diese vielfältige Materiallandschaft verarbeiten können, einschließlich gemischter Kunststoffabfälle, die sonst auf Deponien landen würden. Unsere Ingenieure wissen, dass sich verschiedene Materialien bei der Verarbeitung unterschiedlich verhalten. Kunststoffextrusionsverfahrendie spezifische Temperaturprofile, Schneckenkonstruktionen und Kühlmethoden erfordern.
Gemeinsame Anwendungen
Betreten Sie Ihr Zuhause und sehen Sie sich um - Sie sind umgeben von Produkten der Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren. Die Fußleisten entlang Ihres Fußbodens? Wahrscheinlich ein extrudiertes PVC-Profil. Der aufgerollte Gartenschlauch neben Ihrer Hintertür? Eine weitere Erfolgsgeschichte der Extrusion.
Die Bauindustrie hat extrudierte Kunststoffe mit besonderer Begeisterung aufgenommen. Fensterrahmen und Bauprodukte aus Hart-PVC bieten eine hervorragende Isolierung und Witterungsbeständigkeit, ohne die Wartungsprobleme von Holz zu verursachen. Wenn Sie durch eine moderne Wohnsiedlung spazieren, werden Sie Vinylverkleidungen, Regenrinnen und dekorative Verkleidungen sehen - alles durch Extrusion hergestellt.
Unterirdisch, Rohre und Schläuche bilden die unsichtbare Infrastruktur des modernen Lebens. Von massiven städtischen Wasserleitungen bis hin zu den empfindlichen Bewässerungsleitungen in Ihrem Garten transportieren extrudierte Rohre alles, vom Trinkwasser bis zum Abfall. Medizinische Einrichtungen verlassen sich auf präzise extrudierte Rohre für die Verabreichung von Medikamenten, den Abtransport von Flüssigkeiten und unzählige andere kritische Anwendungen, bei denen Konsistenz und Sauberkeit nicht verhandelbar sind.
Die Verpackungsindustrie wäre nicht mehr wiederzuerkennen ohne Folien und Platten erstellt durch die Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren. Diese Schutzhüllen halten Ihre Lebensmittel frisch? Extrudierte Folien. Die Blisterverpackungen, die Ihre neue Elektronik schützen? Sie wurden oft als extrudierte Folien hergestellt, bevor sie thermogeformt wurden. Landwirtschaftliche Folien, die den Landwirten helfen, die Vegetationsperiode zu verlängern und den Wasserverbrauch zu senken? Sie haben es erraten - Produkte der Extrusionstechnologie.
Moderne Elektronik ist stark abhängig von Draht- und Kabelisolierung die durch Ummantelungsextrusion hergestellt werden. Dieses spezielle Verfahren umhüllt Metallleiter mit schützenden Kunststoffschichten und ermöglicht eine sichere und zuverlässige Stromverteilung in unseren Häusern, Fahrzeugen und Geräten.
Was uns bei JianTai Plastic Machinery Company am meisten begeistert, ist zu sehen, wie unsere Kunden Kunststoffabfälle in wertvolle neue Produkte verwandeln. Diese Parkbänke aus recyceltem Kunststoff? Die Landschaftsbauhölzer, die nie verrotten? Die langlebigen Außenmöbel, die jahrelang dem Wetter trotzen? All das ist möglich, weil die Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren kann Materialien, die sonst auf der Mülldeponie landen würden, neues Leben einhauchen.
Durch die Bereitstellung von Maschinen, die recycelte Kunststoffe effizient verarbeiten, helfen wir Herstellern, ihre Rohstoffkosten zu senken und gleichzeitig einen positiven Beitrag zum Umweltschutz zu leisten. Eine Win-Win-Situation, die zeigt, welch wichtige Rolle die Extrusionstechnologie beim Aufbau einer nachhaltigeren Zukunft spielt - ein Profil, ein Rohr oder eine Folie nach der anderen.
Vorteile und Nachteile des Kunststoffextrusionsverfahrens
Wenn Sie Fertigungsmethoden für Ihre Kunststoffprodukte in Betracht ziehen, ist es wichtig, die Stärken und Grenzen der einzelnen Verfahren zu kennen. Die Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren bietet einige überzeugende Vorteile, die sie zu einem Eckpfeiler der modernen Fertigung gemacht haben, aber sie bringt auch Nachteile mit sich, die es zu berücksichtigen gilt.
Vorteile des Kunststoffextrusionsverfahrens
Die Schönheit der Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren liegt in seiner Effizienz und Skalierbarkeit. Im Gegensatz zu Batch-Prozessen, die starten und stoppen, läuft die Extrusion kontinuierlich und ermöglicht es den Herstellern, unglaublich lange Materialbahnen ohne Unterbrechung zu produzieren. Dieser kontinuierliche Betrieb schlägt sich direkt in beeindruckenden Produktionsmengen nieder, die nur wenige andere Verfahren erreichen können.
"Extrusionsmaschinen können kontinuierlich arbeiten und so eine gleichmäßige Produktion und hohe Produktionsraten gewährleisten", so ein Hersteller. Dieser Non-Stop-Betrieb bedeutet, dass Sie Ihre Produktion maximieren und gleichzeitig die Arbeitskosten minimieren können - eine Win-Win-Situation für Produktionsleiter, die auf ihr Endergebnis achten.
Aus finanzieller Sicht bietet die Extrusion in der Regel ein ausgezeichnetes Kosten-Nutzen-Verhältnis, vor allem bei mittleren bis hohen Stückzahlen. Die Werkzeugkosten für Werkzeuge sind im Allgemeinen erschwinglicher als komplexe Spritzgussformen, und die kontinuierliche Natur des Prozesses bedeutet weniger Bedienereingriffe und geringere Arbeitskosten pro produzierter Einheit.
Einer der attraktivsten Aspekte des Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren ist seine Vielseitigkeit. Ein und dieselbe Anlage kann oft mit nur geringfügigen Anpassungen ein breites Spektrum an thermoplastischen Materialien verarbeiten, was den Herstellern eine enorme Flexibilität bietet. Diese Anpassungsfähigkeit erstreckt sich auch auf die Produkte selbst - extrudierte Kunststoffe können noch im warmen Zustand bearbeitet werden, was zusätzliche Formgebung, Prägung oder andere Modifikationen ermöglicht, die das Endprodukt aufwerten.
Auch Umweltaspekte sprechen für die Extrusion. Das Verfahren erzeugt nur minimale Abfälle, und die wenigen Abfälle, die anfallen, können in der Regel wieder gemahlen und direkt in den Trichter zurückgeführt werden. Dieser geschlossene Fertigungskreislauf passt perfekt zu den heutigen Nachhaltigkeitszielen und kann die Materialkosten im Laufe der Zeit erheblich senken.
Für Hersteller, die verschiedene Materialien oder Farben kombinieren müssen, ermöglicht die Coextrusion die gleichzeitige Extrusion mehrerer Materialien, wodurch Produkte mit unterschiedlichen Eigenschaften oder Erscheinungsbildern in einem einzigen Durchgang durch die Maschine entstehen.
Nachteile des Kunststoffextrusionsverfahrens
Trotz seiner vielen Vorteile ist das Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren ist nicht die richtige Lösung für jede Fertigungsaufgabe. Die größte Einschränkung besteht darin, dass beim Strangpressen nur Teile mit einem gleichmäßigen Querschnitt über die gesamte Länge hergestellt werden können. Wenn Sie komplexe dreidimensionale Formen benötigen, sind entweder zusätzliche Bearbeitungsschritte oder ein ganz anderes Herstellungsverfahren erforderlich.
Bei der Arbeit mit extrudiertem Kunststoff müssen einige schwierige physikalische Eigenschaften berücksichtigt werden. Die Schwellung ist eine häufige Herausforderung - Kunststoff neigt dazu, sich nach dem Verlassen des Werkzeugs leicht auszudehnen, was bedeutet, dass Ingenieure Werkzeuge entwerfen müssen, die diese Ausdehnung kompensieren. Wenn der heiße Kunststoff abkühlt, kann er zudem schrumpfen oder sich verziehen, was die endgültigen Abmessungen Ihres Produkts beeinträchtigen kann.
Obwohl sie im Allgemeinen erschwinglicher sind als die Einrichtungskosten für das Spritzgießen, können die Anfangsinvestitionen in Werkzeuge und Ausrüstungen immer noch beträchtlich sein, insbesondere bei Spezialanwendungen. Diese Vorlaufkosten müssen bei der Produktionsplanung und den ROI-Berechnungen berücksichtigt werden.
Bei Produkten, bei denen es auf das Aussehen ankommt, ist zu beachten, dass extrudierte Artikel sichtbare Linien oder andere Oberflächenfehler aufweisen können. Diese können bei ästhetisch kritischen Anwendungen eine sekundäre Nachbearbeitung erfordern, was den Herstellungsprozess zeit- und kostenaufwändig macht.
Auch bei der Materialauswahl gibt es einige Einschränkungen. Obwohl sich viele Thermoplaste hervorragend extrudieren lassen, erfordern einige Hochleistungspolymere eine spezielle Ausrüstung oder sind möglicherweise überhaupt nicht für die Extrusion geeignet.

"Wenn man die Kunststoffextrusion mit dem Spritzgießen vergleicht", so ein Branchenexperte, "ist die Extrusion ideal, wenn ein einheitliches Querschnittsprofil für verschiedene Produkte erforderlich ist, während das Spritzgießen sich durch die Herstellung vollständig geformter dreidimensionaler Teile auszeichnet.
Bei JianTai Plastic Machinery Company helfen wir unseren Kunden, diese Überlegungen zu steuern, um festzustellen, ob die Extrusion die richtige Lösung für ihre spezifischen Anforderungen ist. Wir berücksichtigen Faktoren wie Anforderungen an das Produktionsvolumen, Materialspezifikationen und Produktkomplexität, bevor wir Lösungen empfehlen. Unsere Erfahrung mit Kunststoffrecyclinganlagen hat vielen Unternehmen geholfen, Abfallstoffe in wertvolle Produkte umzuwandeln, und zwar durch die Kunststoffextrusionsverfahrendie sowohl ökologische als auch wirtschaftliche Vorteile mit sich bringen.
Umweltaspekte und Nachhaltigkeit
Wenn wir über die Kunststoffextrusionsverfahrengeht es nicht nur um ein Herstellungsverfahren, sondern um eine potenzielle Lösung für eines der drängendsten Probleme unseres Planeten: Plastikmüll.
Die Realität ist ernüchternd, aber motivierend. In einem Branchenbericht heißt es: "Wir alle sind in irgendeiner Form mit Plastikmüll in Berührung gekommen. Man findet ihn in unseren Häusern, auf unseren Straßen und in unseren Ozeanen." Diese weit verbreitete Präsenz von Plastikmüll ist nicht nur ein Problem, sondern auch eine Chance für Innovationen und positive Veränderungen.
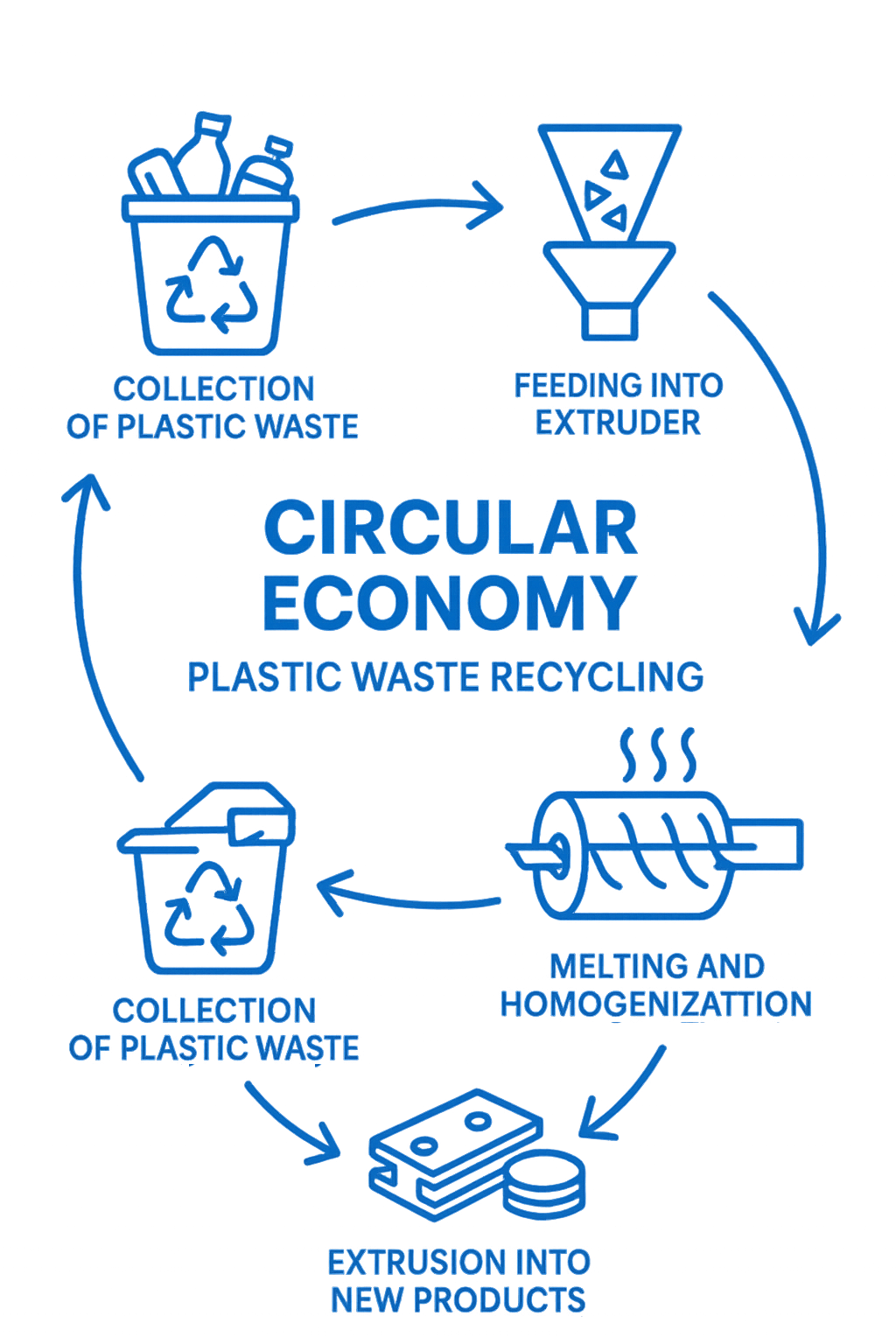
Hier zeigt sich die Schönheit der Extrusionstechnologie am deutlichsten. Die Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren ist in einer einzigartigen Position, um in der Kreislaufwirtschaft die Rolle des Helden zu spielen, indem es Kunststoffabfällen ein zweites Leben gibt - oder sogar ein drittes oder viertes!
Bei JianTai Plastic Machinery Company haben wir erlebt, wie die Extrusion die Bemühungen um Nachhaltigkeit verändern kann. Wir haben spezielle Anlagen entwickelt, die das, was andernfalls eine Belastung für die Umwelt darstellen würde - Post-Consumer- und Post-Industrial-Kunststoffabfälle - in wertvolle neue Produkte umwandeln, die in unserem täglichen Leben einen echten Nutzen haben.

Unsere zweistufige Ein-Schritt-Extrudermaschine für das Kunststoffrecycling verkörpert diese Philosophie in der Praxis. Dieses System ist ein Wendepunkt, denn es eliminiert unnötige Schritte im Recyclingprozess. Anstatt mehrere Maschinen und energieintensive Zwischenprozesse zu benötigen, kann es gemischte Kunststoffabfallfolien direkt in Fertigprodukte umwandeln.
Das Besondere an dieser Technologie ist ihr durchdachtes Design. Unser fortschrittliche Fütterungssysteme kann mit der chaotischen Realität gemischter Kunststoffabfälle umgehen - Materialien, die andernfalls als "zu schwierig" für das Recycling gelten würden. Die spezielle Schneckenausführung mit variabler Durchmessertechnologie sorgt dafür, dass selbst gemischte Materialien gründlich gemischt werden, um eine gleichbleibende Qualität zu gewährleisten. Inzwischen, präzise Kontrollsysteme mit SPS-Automatisierung die Produktqualität unabhängig von Eingangsschwankungen aufrechterhalten und energieeffizient Heiz- und Kühlsysteme minimieren den ökologischen Fußabdruck des Recyclingprozesses selbst.
Der Gewinn für die Umwelt ist erheblich und vielschichtig. Indem wir Plastik von den Mülldeponien und Ozeanen fernhalten, gehen wir das Abfallproblem direkt an. Indem wir den Bedarf an neuen Kunststoffen verringern, schonen wir wertvolle Ressourcen. Auch die Energieeinsparungen sind beträchtlich: Für das Recycling von Kunststoff werden in der Regel 66% weniger Energie benötigt als für die Herstellung von neuem Kunststoff. All dies führt zu einer erheblichen Verringerung des CO2-Fußabdrucks im Vergleich zur herkömmlichen Herstellung mit neuen Materialien.
"Die Kunststoffextrusion wird als kosteneffiziente Alternative zu anderen Verfahren der Kunststoffumformung dargestellt, insbesondere für gleichförmige 2D-Produkte", wie Branchenexperten festgestellt haben. Diese wirtschaftliche Tragfähigkeit ist von entscheidender Bedeutung, denn wenn Nachhaltigkeitsinitiativen wirklich erfolgreich sein sollen, müssen sie auch wirtschaftlich sinnvoll sein.
Über das Recycling hinaus entwickelt sich die Extrusionsindustrie auf spannende Weise weiter, um die Nachhaltigkeit zu fördern:
Moderne Extrusionsanlagen umfassen heute energieeffiziente Funktionen wie drehzahlvariable Antriebe, die den Stromverbrauch an den tatsächlichen Bedarf anpassen, verbesserte Isolierung, die die Wärme dort hält, wo sie hingehört, und Wärmerückgewinnungssysteme, die Wärmeenergie auffangen und wiederverwenden, die sonst verschwendet würde.
Auch die Wassereinsparung ist zu einer Priorität geworden, mit Kühlsysteme mit geschlossenem Kreislauf die Wasserbilanz von Extrusionsprozessen drastisch zu reduzieren. Und für diejenigen, die keine erdölbasierten Kunststoffe mehr verwenden wollen, sind viele Extruder jetzt für die Verarbeitung von biologisch abbaubare oder biobasierte Kunststoffeund öffnet die Türen zu alternativen Stoffströmen.
Auch der Produktionsprozess selbst ist nachhaltiger geworden, mit fortschrittliche Prozesskontrollen die den Abfall bei der Inbetriebnahme minimieren und eine gleichbleibende Qualität gewährleisten, wodurch die Menge des bei der Herstellung anfallenden Ausschusses reduziert wird.
Bei JianTai ist Nachhaltigkeit nicht nur ein Schlagwort - es ist das Herzstück unseres Unternehmens. Von unserem Sitz in Yuyao City in der Provinz Zhejiang aus haben wir uns der Herstellung von Maschinen verschrieben, die nicht nur Kunststoff verarbeiten, sondern auch dazu beitragen, unsere Beziehung zu diesem vielseitigen, aber problematischen Material zu heilen.
Unsere Mission geht über den Bau von Maschinen hinaus. Wir bauen an einer Zukunft, in der Kunststoffabfälle zu einer wertvollen Ressource werden und nicht zu einer Umweltbelastung. Indem wir unseren Kunden helfen, Abfall in Wert zu verwandeln, unterstützen wir die Kreislaufwirtschaft und helfen ihnen gleichzeitig, ihre Produktionskosten zu senken - und beweisen damit, dass das, was gut für den Planeten ist, auch gut fürs Geschäft sein kann.
Die wissenschaftliche Forschung bringt den Bereich des Kunststoffrecyclings durch Extrusion weiter voran. Studien, die von Organisationen wie TWI Global veröffentlicht wurden, haben gezeigt, dass ordnungsgemäß verarbeitete recycelte Kunststoffe in vielen Anwendungen vergleichbare mechanische Eigenschaften wie Neuware aufweisen können, wodurch sich noch mehr Möglichkeiten für eine nachhaltige Produktion eröffnen.
Wissenschaftliche Forschung zum Recycling beim Strangpressen
Schlussfolgerung
Die Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren steht für eine perfekte Mischung aus technischer Präzision, Fertigungseffizienz und Anpassungsfähigkeit. Vom Einfüllen der Rohstoffe in den Trichter bis zur abschließenden Kühlung und dem Schneiden der fertigen Produkte arbeitet jeder Schritt harmonisch zusammen, um die unzähligen extrudierten Artikel herzustellen, auf die wir uns jeden Tag verlassen.
Im Laufe dieser Erkundung der Kunststoffextrusion haben wir gesehen, dass dieses bemerkenswerte Verfahren den Herstellern erhebliche Vorteile bietet. Die kontinuierliche Natur der Extrusion macht sie ideal für die Großserienproduktion, während ihre Vielseitigkeit die Verarbeitung von Neukunststoff bis hin zu recycelten Materialien ermöglicht. Diese Anpassungsfähigkeit wird immer wertvoller, da sich unsere Welt zunehmend auf Nachhaltigkeit und Ressourcenschonung konzentriert.
Bei JianTai Plastic Machinery Company erleben wir jeden Tag die transformative Kraft der Extrusionstechnologie. Unsere Kunden nutzen unsere Anlagen, um aus sonstigem Kunststoffabfall wertvolle neue Produkte zu machen - von Baumaterialien bis hin zu Haushaltsgegenständen. Diese praktische Anwendung der Kreislaufwirtschaft hilft nicht nur der Umwelt, sondern schafft auch neue Geschäftsmöglichkeiten und Arbeitsplätze.
Kunststoff-Extrusion glänzt durch seine Fähigkeit, Effizienz und Nachhaltigkeit in Einklang zu bringen. Moderne Extrusionsanlagen können enge Toleranzen einhalten und gleichzeitig den Energieverbrauch minimieren, was sie sowohl zu einer wirtschaftlich als auch zu einer ökologisch sinnvollen Investition macht. Das Verfahren erzeugt nur minimale Abfälle, und der anfallende Ausschuss kann in der Regel wieder gemahlen und dem System zugeführt werden - ein perfektes Beispiel für einen geschlossenen Produktionskreislauf.
Mit Blick auf die Zukunft sehen wir spannende Entwicklungen am Horizont für die Kunststoffextrusionsverfahren. Fortschritte in der Automatisierung, Materialwissenschaft und Prozesssteuerung machen die Extrusion noch effizienter und leistungsfähiger. Wir bei JianTai sind stolz darauf, an der Spitze dieser Innovationen zu stehen, insbesondere bei der Entwicklung von Technologien, die gemischte Kunststoffabfallströme verarbeiten können, die bisher nur schwer zu recyceln waren.
Der Weg vom Kunststoffgranulat zum fertigen Produkt mag einfach erscheinen, doch dahinter verbergen sich jahrzehntelange technische Raffinesse und wissenschaftliche Erkenntnisse. Durch die Beherrschung dieses Prozesses können Hersteller nicht nur hochwertige Produkte herstellen, sondern auch eine entscheidende Rolle bei der Bewältigung eines der drängendsten Umweltprobleme unserer Zeit spielen - dem Kunststoffabfall.
Wir laden Sie ein, sich uns bei dieser wichtigen Arbeit anzuschließen. Ganz gleich, ob Sie einen Recyclingbetrieb gründen oder Ihr bestehendes Extrusionsverfahren verbessern möchten, JianTai Plastic Machinery Company bietet Ihnen das Fachwissen und die Ausrüstung, um Ihnen zum Erfolg zu verhelfen. Gemeinsam können wir Kunststoffabfälle von einem Umweltproblem in eine wertvolle Ressource verwandeln.
Weitere Informationen über unsere Kunststoffextrusionsmaschinen und wie sie Ihrem Betrieb nutzen können, finden Sie unter Kunststoff-Extrusionsmaschine: Recyceln mit Präzision.



